Why Is New Car Waiting Time Four Times Longer Than in the US?
Hyundai's Domestic Sales Share at Lowest Since 2016
Due to Increased High-Profit Overseas Sales Share
[Asia Economy Reporter Choi Dae-yeol] Hyundai Motor Company's domestic sales ratio this year has fallen below 40%. This is the lowest level since 2016, which is interpreted as a result of the company judging that selling overseas is more profitable than domestically due to exchange rate effects.
As a result, complaints have erupted that Korean consumers are being discriminated against compared to the U.S. For example, if you order a popular Genesis model now, Korean consumers can only receive it after 2 years and 6 months, whereas in the U.S., it can be received within 7 to 8 months.
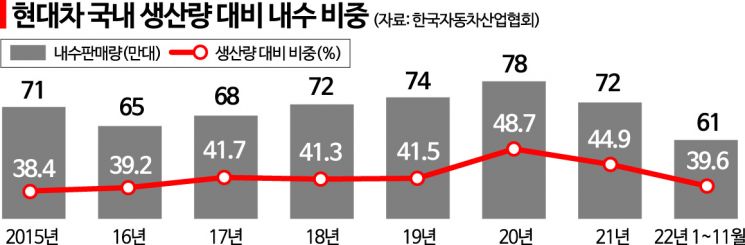
According to statistics from the Korea Automobile Manufacturers Association on the 29th, the total number of finished vehicles produced at Hyundai's domestic factories (including Ulsan, Asan, Jeonju, and consignment production in Gwangju) from January to November this year was 1,561,698 units. Among these, the domestic sales volume sold to Korean consumers was 618,542 units, accounting for 39.6%. The domestic sales ratio of Hyundai's domestic factory production volume has consistently remained above 40% since 2017. In 2020, when overseas transportation was difficult due to COVID-19, it increased to 48.7%, but has been steadily declining since then. This is the first time in six years that the domestic sales ratio has fallen below 40%.
Hyundai, which accounts for about half of the domestic finished car market, has focused more on overseas markets than the domestic market, which appears to be due to the impact of the Korean won's value falling to its lowest level since the 1990s foreign exchange crisis. As the representative foreign currency, the dollar has become more expensive, so even when selling the same car, selling overseas yields more profit than domestically. It is reported that when Hyundai conducts overseas transactions, about half of the transactions are in dollars, and every 1 won increase in the won-dollar exchange rate affects profits by about 30 billion won.
Amid severe supply shortages of various parts such as vehicle semiconductors due to COVID-19, production disruptions and delivery backlogs continue. As supply cannot keep up with vehicle demand, a supplier's market has formed, creating conditions where companies can 'choose' their customers.
The parts shortage is a common problem faced by finished car manufacturers worldwide, and although there were signs of some easing this year, it has not been completely resolved due to the Russia-Ukraine war and strengthened quarantine measures in some regions such as China. The relatively high popularity of expensive electric vehicles among high-end brands like Genesis and Hyundai in North America and Europe also played a role.
In a global situation where semiconductor supply is not smooth, there is evidence that Hyundai prioritized parts for the North American market, which is relatively more profitable. According to data from market research firm AutoForecast Solutions, most finished car factories in North and Central America are expected to experience production disruptions of thousands to tens of thousands of units, whereas Hyundai and Kia have no expected production disruptions at all. The only factories with zero potential production disruptions include Hyundai, Kia, Daimler, and the local consignment production factory Compass. Hyundai and Kia produce about 1.1 million units annually combined at their plants in Alabama and Georgia in the U.S., and Nuevo Le?n in Mexico.
There are also criticisms about differences in waiting periods after ordering new cars. As of early this month, customers are informed that ordering a Genesis GV80 domestically takes up to 2 years and 6 months (based on the gasoline 2.5T model). Other Genesis vehicles have a minimum wait of one year. According to local U.S. communities, large models like the GV80 take 7 to 8 months, and other models less than 6 months. Except for the electric GV70, Genesis vehicles are all assembled in Korea and exported as Korean-made cars. Considering that export models have simpler configurations in options and colors, the delivery period difference is still quite significant.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.


!["The Woman Who Threw Herself into the Water Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag"...A Grotesque Success Story That Shakes the Korean Psyche [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















