Consumer Risk Factors ▲ Continued Inflation ▲ Interest Rate Hikes ▲ Tax and Utility Burden
[Asia Economy Reporter Park Sun-mi] Household consumption, which has served as a safety net for our economy, is expected to remain sluggish next year due to concerns over high inflation and income reduction caused by the economic downturn, according to a recent survey.
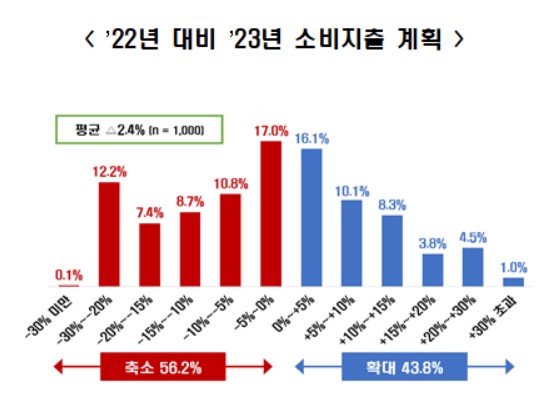
On the 6th, the Federation of Korean Industries (FKI) commissioned a survey through the polling agency Mono Research targeting 1,000 adults aged 18 and over nationwide to investigate the '2023 National Consumption Expenditure Plan.' The results showed that 56.2% of respondents plan to reduce their consumption expenditure next year compared to this year. The FKI forecasted that household consumption expenditure will decrease by an average of 2.4% next year compared to this year.
By income quintile, only the top 20% income group (5th quintile) is expected to increase consumption expenditure (+0.8%), while the remaining lower 80% income groups (1st to 4th quintiles) are all expected to reduce consumption expenditure. In particular, consumption expenditure in the 1st to 4th quintiles is expected to decline by 6.5%, 3.1%, 2.0%, and 0.8%, respectively, showing a larger decrease as income decreases. This is because lower-income groups are more affected by employment and income reductions due to high inflation and economic recession, proportionally reducing their consumption capacity.
The main reason cited by the public for reducing consumption expenditure next year was price increases (43.9%). Concerns about job loss and income reduction (13.5%), tax and utility burdens (10.4%), and debt (loan principal and interest) repayment burdens (10.3%) followed. By category, respondents said they would reduce spending on travel, dining out, and accommodation (21.0%), durable goods (15.4%), and leisure and cultural activities (15.0%).
Risk factors that could affect consumption activities next year include continued inflation (46.0%), interest rate hikes (27.0%), increased tax and utility burdens (11.9%), and contraction in asset markets such as real estate and stocks (8.9%).
Meanwhile, the majority (74.5%) of the public expressed concerns that the intensity of the economic recession will increase next year and expected household financial conditions to worsen compared to this year. Only 25.5% of respondents believed their household financial situation would improve. Six to seven out of ten people (65.3%) responded that they lack sufficient consumption capacity to carry out their planned consumption next year, considering inflation and debt situations. To secure additional consumption capacity, respondents cited side jobs (35.7%), withdrawing savings (22.6%), and selling financial assets such as stocks (17.9%).
Choo Kwang-ho, head of the FKI Economic Department, stated, “If low growth in the 1% range materializes next year amid ongoing high inflation and high interest rates, there is a risk that household consumption fundamentals will deteriorate.” He added, “The government needs to expand the capacity for job maintenance and creation by revitalizing corporate activities to preserve household income, which is the core of private consumption.”
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















