HIRA Analyzes 10 Years of Medical Utilization Statistics for Spine and Joint Diseases
[Asia Economy Reporter Jo In-kyung] More than one in five Koreans have received treatment for spinal diseases. As the number of young patients increases, the average age at diagnosis continues to decrease.
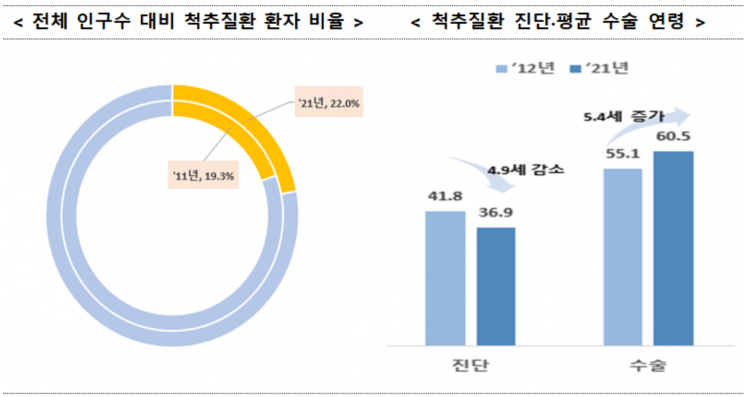
According to the analysis of medical use for spinal and joint diseases released by the Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service on the 29th, the total number of spinal disease patients in Korea last year was 11.31 million, accounting for 22.0% of the total population. The proportion of spinal disease patients relative to the population increased by 2.7 percentage points compared to 19.3% in 2011.
The average age at diagnosis has steadily decreased from 41.8 years in 2012 to 36.9 years in 2021. Among the 1.18 million new patients last year, 470,000, or 40%, were young people in their 20s and 30s.
The total number of spinal surgeries performed last year was 128,000, with an average surgery age of 60.5 years, which is 5.4 years higher than in 2012. The proportion of surgeries within three years after diagnosis decreased from 45.3% in 2012 to 9.9% in 2021, while the proportion of surgeries performed more than five years after diagnosis increased from 21.5% to 85.5% during the same period, a rise of 64.0 percentage points, indicating that the timing of surgery after diagnosis has been extended.
Along with spinal diseases, joint diseases, which commonly occur in modern people, had 7.36 million patients last year, accounting for 14.3% of the total population. The proportion of joint disease patients also increased by 2.1 percentage points compared to 2011, and the average age at diagnosis decreased from 44.7 years in 2012 to 41.8 years in 2021.
Among the 1.14 million new joint disease patients in 2021, those in their 50s were the largest group, with 230,000 patients, accounting for 20.2%.
Last year, 67,770 knee replacement surgeries and 3,277 hip replacement surgeries were performed, with average surgery ages of 71.1 years and 64.2 years, respectively.
In musculoskeletal diseases, non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy are also widely used besides surgery. By treatment type, oral medication such as analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs accounted for the highest proportion at 72.7%, followed by physical therapy at 43.3%, injection therapy at 38.7%, Korean medicine procedures at 34.2%, nerve block therapy at 26.7%, rehabilitation therapy at 20.8%, and intra-articular injections and other injection pain treatments at 15.6%.
The Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service forecasted that the number of spinal and joint disease patients will continue to increase, as the elderly population with functional decline grows due to longer average lifespans, and the prevalence among younger age groups rises due to factors such as work environment and lifestyle habits.
An Mira, head of the Benefit Information Analysis Office at the Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service, advised, "It is necessary to adopt lifestyle habits that prevent musculoskeletal diseases in daily life and to consistently practice moderate exercise for management."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.