2020 Overall Hospitalization Rate Decreased by 86% Compared to Previous Year
Social Distancing After COVID-19 Affected Accident Cases and Medical Institution Visit Frequency
[Asia Economy Reporter Byeon Seon-jin] Since COVID-19, the number of patients hospitalized or taken to emergency rooms due to accidents has significantly decreased compared to before. It is analyzed that the reduction in outdoor activities due to social distancing also affected the number of accidents and the frequency of medical institution use.
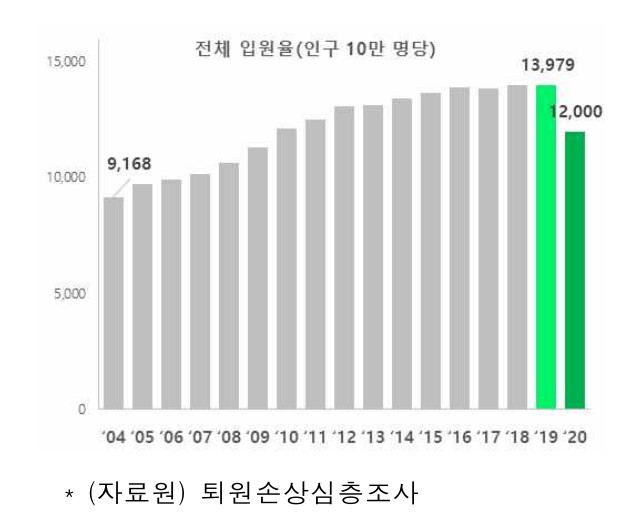
On the 30th, the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA) announced the main results of the 'Discharge Injury In-depth Survey' targeting hospitalized patients in 2020 and last year's 'Emergency Room Injury Patient In-depth Survey.' According to the main results, the overall hospitalization rate per 100,000 population in 2020 was 12,000, a decrease of 86% compared to the previous year (13,979). The injury hospitalization rate in 2020 was also 2,014, down 90% from 2,250 in 2019. Injuries refer to physical and mental health problems caused by accidents, poisoning, etc.
The proportion of injury patients among all hospitalized patients was 16.8%, ranking first among all disease groups. The injury hospitalization rate for men was 2,165, higher than that for women (1,863), and it tended to increase with age, with those aged 75 and older accounting for 6,211. By cause of injury, the hospitalization rate due to falls was the highest at 791 per 100,000 population, followed by transport accidents at 469. The injury hospitalization rate due to transport accidents has been declining annually since 2015 (738), with a decrease of 100 per 100,000 population (17.6%) in one year from 569 in 2019 to 469 in 2020. Among other causes of injury, cancer patients accounted for 12.3%, digestive system disease patients 11.4%, and circulatory system disease patients 8.9%, in that order.
The number of injury patients visiting emergency rooms also showed a continuous decline: 277,372 in 2019, 206,887 in 2020, and 190,496 last year. Among injury patients who visited emergency rooms last year, 27.1% were fall patients, the highest proportion, followed by blunt trauma (19.0%) and transport accident (13.9%) patients in second and third place.
Among ages 0-9, fall injuries (42.5%) and blunt trauma (29.0%) were common. In the 10-30 age group, transport accident patients increased compared to ages 0-9, while fall injury patients decreased. In teenagers, blunt trauma patients accounted for 25.2%, higher than fall injuries (23.6%), and in their 20s, stab wound patients were the most common at 20.4%. Patients in their 30s showed similar proportions: blunt trauma 20.1%, fall injuries 19.6%, transport accidents 18.4%, and stab wounds 18.5%.
The KDCA explained, "An additional analysis of the activities at the time of injury for emergency room injury patients showed that falls mainly occurred during daily life, leisure activities, or work." Regarding the decrease in injury patients after COVID-19, it was diagnosed that "this reflects changes in social activities and medical institution use due to the COVID-19 pandemic."
The main results announced by the KDCA as part of the injury survey monitoring project will be used as a basis for injury prevention management strategies. Kim Hyun-jun, deputy director of the KDCA, said, "We will strengthen the capacity to analyze injury risk factors and vulnerable groups to promote scientific evidence-based injury prevention management projects using injury survey monitoring data."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.