Over 400 Billion Won in Damage from Cyber Attacks on Shipping Companies Including Maersk
Domestic Top 3 Shipbuilders Develop and Certify Cybersecurity Solutions for Preparedness
The wave of the 4th Industrial Revolution is heating up the maritime shipping market. Just as drivers take their hands off the steering wheel, helmsmen and navigators are now entering an era where they can take their hands off the rudder. In fact, shipbuilding has become much more complex. Ship construction, which involves not only internal fuel tanks and piping but also electronic devices and electrical equipment that control and manage the entire vessel, has become increasingly challenging.
◆ Autonomous Navigation Era, Cyberattack Threats Increase = According to industry sources on the 30th, the three major domestic shipbuilders are equipped with autonomous navigation solutions, automatic docking systems, and augmented reality-based navigation, possessing technology corresponding to the second stage of autonomous navigation.
Behind the introduction of 4th Industrial Revolution technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), big data, and artificial intelligence (AI) in the maritime shipping sector lies the threat of cybersecurity. If remote control technology is not secured for cyber safety, it is highly likely to lead to major maritime accidents. Ship accidents not only damage national or corporate interests but can also result in large-scale casualties. Maritime accidents can cause secondary damage due to the sea's water temperature in evacuation areas and are said to cause damage approximately six times more severe than road traffic accidents.
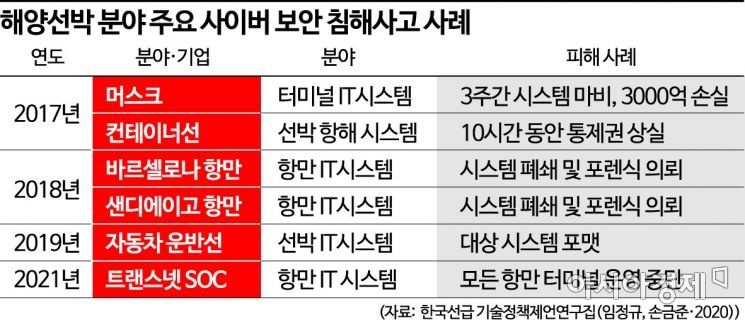
The threat of cybersecurity has been confirmed through actual cases. In January 2018, the world's largest shipping company, Maersk, suffered a ransomware attack called 'Petya,' which paralyzed its IT and operational control systems for a while. This caused the suspension of operations at 76 port terminals and required the reinstallation of 4,000 servers and 45,000 PCs. The economic loss amounted to 300 million dollars (approximately 430.3 billion KRW).
In February 2017, pirates hacked the navigation system of a German container ship (8250 TEU) sailing from Cyprus to Djibouti, rendering it uncontrollable for 10 hours. They manipulated the navigation system to steer the ship to a location of their choosing with the intent to hijack the vessel.
Accordingly, the three major domestic shipbuilders are accelerating the development of cybersecurity solutions and international certifications. As the era of autonomous navigation approaches, preparations for cybersecurity are also necessary.
◆ The Three Major Shipbuilders Accelerate Cybersecurity = Hyundai Heavy Industries Group has obtained basic certifications from five different classification societies, the most in the ship cybersecurity field. The recently approved ship is an 84,000 cubic meter (㎥) LPG carrier built by Hyundai Heavy Industries Group, with technology certified to safely protect navigation, communication systems, and overall ship control systems from internal and external cybersecurity threats.
Hyundai Heavy Industries Group received cybersecurity certification for large vessels from the American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) in 2018. Subsequently, it obtained certifications sequentially from the UK (LR), Norway (DNV), Korea (KR), and most recently France (BV), totaling five classification societies. Based on this, the group is leading technology development and standard establishment for autonomous ships.
Samsung Heavy Industries also acquired 'Smart Ship Cybersecurity Technology' certification from ABS. Last year, it received a certificate of results for a 'Ship Cybersecurity Simulator' from the Korean Register. This simulator is a testbed developed by Samsung Heavy Industries considering the cybersecurity of smart ships. It even has its own test system to prepare for cyberattacks.
Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering successfully developed a smart ship platform independently in 2019. Since then, through its land-based control center at the Siheung R&D Campus, it provides various data services required by shipowners for vessels in operation. The company's smart ship solution has been adopted as a basic requirement in the construction specifications of all contracted ships.
International organizations have also begun establishing management systems for cybersecurity. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has mandated the establishment of cybersecurity risk management systems for international navigation vessels through 'Cyber Risk Management (MSC)' since January 1, 2020, and cybersecurity certifications are being conducted mainly by representative classification societies including the Korean Register.
Leading countries in the shipping sector, including the United States and the EU, have already revised related laws and are strengthening ship security. In December 2020, the United States announced the 'National Maritime Cybersecurity Strategy,' emphasizing the enhancement of maritime cyber threat intelligence R&D and cooperation, investigation of ship cybersecurity threats, and public-private-military cooperation for ship cybersecurity investigations.
In South Korea, the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries began research on ship cybersecurity through the 'Maritime (Ship Safety) Cybersecurity Policy Study' in 2020 and recently started collecting, analyzing, and managing cybersecurity threats inside and outside ships. Additionally, through partial amendments to the 'Act on Promotion of Information and Communications Network Utilization and Information Protection,' ships have become subject to information protection regulations.
Professor Kim Seok-gyun of the Department of Maritime Police at Hanseo University pointed out, "For South Korea, which is absolutely dependent on maritime transport, maritime cybersecurity is an urgent issue," and emphasized, "The government must establish countermeasures and response guidelines."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.