South Korean battery companies are thoroughly excluding China amid global supply chain changes surrounding the United States' Inflation Reduction Act (IRA).
On the 4th, Asia Economy examined the supply and demand changes in the supply chains of seven major battery companies for the second half of this year (after July) and found that out of 10 cases, only one involved newly sourcing key battery raw materials or components from China.
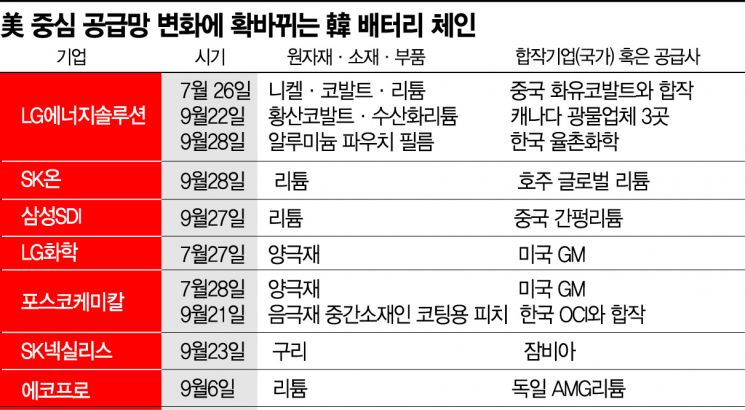
This case involves LG Energy Solution establishing a joint venture with Huayou Cobalt in China to extract lithium, nickel, cobalt, and other materials from used batteries for raw material procurement. These raw materials are scheduled to be supplied to LG Energy Solution's battery factory located in Nanjing, China.
The most notable trend is the diversification of supply chains by sourcing raw materials from North America, Europe, Africa, and Australia (4 cases). SK On recently agreed to procure lithium concentrate (spodumene, ore purified of impurities) produced from mines in Australia from the Australian company Global Lithium. Established in 2018, Global Lithium is currently conducting large-scale lithium concentrate development projects at two mines in Australia. The estimated total lithium reserves of these mines are approximately 500,000 tons. Although the agreement is currently at the memorandum of understanding (MOU) stage, with the volume, supply timing, and region undecided, Australia is a country that has signed a free trade agreement (FTA) with the United States and is expected to be exempt from the electric vehicle subsidy restrictions stipulated by the Inflation Reduction Act.
LG Energy Solution is also leading supply chain diversification by agreeing to procure 7,000 tons of cobalt sulfate and 255,000 tons of lithium hydroxide from three Canadian mineral companies.
South Korean battery companies have been excessively dependent on imports of key raw materials such as lithium from China. According to the report "Battery Key Raw Material Supply Chain Analysis: Lithium" published by the Korea International Trade Association, South Korea's lithium import share from China was the highest at 64% from January to July this year. It was 47% in 2020 and about 59% last year.
Especially, lithium imports from China this year surged by a staggering 471% to $1.615 billion (approximately 2.3191 trillion KRW) compared to the same period last year. According to the export-import statistics announced by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy in September, imports of precision chemical raw materials (51.8%), which include battery materials and raw materials such as semiconductors, lithium hydroxide, and nickel-cobalt hydroxides?key intermediate goods for domestic industrial production?also increased significantly compared to last year. Amid the U.S.-led supply chain restructuring, the necessity for Korean companies to diversify raw material and component procurement has become more prominent.
Efforts to localize battery components and materials by domestic companies have recently shown promising results. POSCO Chemical established a joint venture, P&OChemical, with OCI to produce pitch for coating, an intermediate material for battery anodes, and is building a factory in Gongju, Chungnam Province. Pitch, a carbon material produced by refining coal or petroleum, is used for surface coating of anodes and as a binder in aluminum smelting processes, significantly impacting battery charging speed and lifespan. Previously, pitch materials were entirely imported, but localization has now been achieved.
LG Energy Solution also agreed to procure aluminum pouch film for electric vehicle batteries from the domestic company Yulchon Chemical. The contract is worth approximately 1.5 trillion KRW over six years from 2023 to 2028. This is the first case of localization and mass production in the battery pouch film sector, which had been virtually monopolized by Japanese companies such as DNP and Showa Denko.
Since the implementation of the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act, the changed supply chain acquisition strategies of Korean companies have become apparent. Notably, seven out of ten recent supply chain changes occurred after the law's enforcement on the 16th of last month. A distancing from the Chinese supply chain is also detected. On the 22nd, Samsung SDI sold 16,622,000 shares (worth about 180 billion KRW) of Ganfeng Lithium, China's largest lithium company. Samsung SDI plans to use the proceeds from this sale to diversify its supply chain.
Professor Kim Pil-su of the Department of Automotive Engineering at Daelim University said, "Not all industries benefit from the supply chain changes led by the U.S., but it is certainly time to change the China-centric supply chain," adding, "Along with companies' efforts to diversify supply chains, diplomatic efforts at the government level should also be made to secure favorable standards for Korean companies in the detailed criteria of the Inflation Reduction Act."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.