Ambiguous Interpretations Put Innovation Finance Designation at a Disadvantage
Even If Approved, Cases of Fraud and Technology Theft Allegations Arise
[Asia Economy Reporters Minwoo Lee, Aeri Boo, Nayoung Shim] “I applied for the Innovative Financial Service designation, but it almost forced me to shut down my business.”
This is the lament of Seung-ik Hwang, CEO of Korea NFC, who has been operating a business since receiving the Innovative Financial Service designation from the Financial Services Commission (FSC) in 2019. Complaints about the FSC’s Innovative Financial Service program continue unabated. The designation criteria and reasons for rejection are unclear and opaque, and there are growing industry grievances that proper management after designation is not being conducted.
Ambiguous Criteria Leave Companies in a Bind
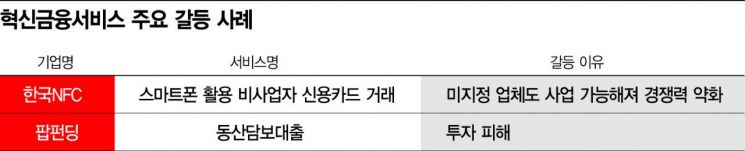
Korea NFC received the Innovative Financial Service designation in May 2019 for its “credit card transactions by non-business individuals using smartphones” service, which allows individual sellers without business registration to accept credit card payments online. It was praised for its potential to contribute to small business startups in various fields such as secondhand trading, food trucks, street vendors, and private tutoring.
Now, two years after launching this service, Korea NFC is facing a crisis of survival. Businesses granted regulatory exemptions under the Innovative Financial Service designation must operate within constraints imposed by the FSC, such as transaction limits, submission of actual transaction verification documents, and copies of ID and bankbooks. However, large platforms operating open markets like Naver and 11st, as well as smaller PG (Payment Gateway) agencies, offer almost identical services allowing non-business individuals to make card payments without any such obligations.
CEO Hwang said, “We spent money to meet about ten additional conditions required by the FSC after receiving various consultations, but it turned out to be a foolish choice. Due to reckless competition, Korea NFC, which followed the formal procedures, is suffering from deteriorating business viability and worsening financial conditions.”
However, large platforms like Naver also have their grounds. According to the ‘E-commerce Notification’ revised by the National Tax Service in 2018, payment gateway companies must verify “history of bad merchants, authenticity of business registration, etc.” when contracting with sellers. Since it does not explicitly state that business registration is mandatory, they argue that their actions are not illegal.
A Naver representative explained, “Allowing individual sellers to accept card payments is a matter that has undergone sufficient legal review. There is no clause in the Specialized Credit Finance Business Act that explicitly prohibits credit card transactions by non-business individuals, and several open markets already support credit card transactions in the same way.” Ultimately, due to ambiguous judgments and management by authorities, only businesses designated as Innovative Financial Service providers have suffered disadvantages.
Suspicions of Fraud and Technology Theft... Vulnerabilities Even After Approval
There are also criticisms regarding gaps in risk and business feasibility assessments. Although these companies carry the title of “businesses recognized by the FSC,” various controversies have persisted for years. The case of Popfunding is a representative example. This company introduced a P2P service that evaluated inventory of home shopping and online shopping sellers to provide loans. However, issues of investment fraud and embezzlement arose, with damages amounting to 137.8 billion KRW.
Popfunding was recognized as an Innovative Financial Service provider when the FSC selected it as a designated agent company in March 2019. At that time, FSC Chairman Eun Sung-soo even visited Popfunding’s logistics warehouse in Paju and praised it as an “innovative case of movable asset financing.”
There have also been troubles due to technology disputes. BC Card received the Innovative Financial Service designation from the FSC for its “QR code-based simple peer-to-peer remittance service,” but a startup named Paxmoney raised allegations of technology theft by BC Card, leading to conflict. BC Card later stated that it is currently operating the service in a form unrelated to Paxmoney’s technology.
Experts point out the need for the FSC to publicize the criteria and processes for Innovative Financial Services more transparently. Professor Jiyong Seo of Sangmyung University’s Business Administration Department said, “Initially, it seemed innovative, but as services were mainly supported for big tech companies like Naver and Kakao, the innovation disappeared. Since the FSC evaluates internally, unforeseen variables and problems arise. There is a need for public discussion or disclosure to gather opinions on what issues exist.”
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![User Who Sold Erroneously Deposited Bitcoins to Repay Debt and Fund Entertainment... What Did the Supreme Court Decide in 2021? [Legal Issue Check]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026020910431234020_1770601391.png)















