Expansion of Plastic Waste Recycling Scope
Electric Vehicle Batteries Exempt from Waste Regulations
 On the morning of the 5th, Yoo Je-cheol, Vice Minister of the Ministry of Environment, is briefing at the Government Sejong Complex in Sejong City on measures to revitalize the circular economy through regulatory improvement support for industries such as plastic pyrolysis and used battery recycling.
On the morning of the 5th, Yoo Je-cheol, Vice Minister of the Ministry of Environment, is briefing at the Government Sejong Complex in Sejong City on measures to revitalize the circular economy through regulatory improvement support for industries such as plastic pyrolysis and used battery recycling.
[Asia Economy Sejong=Reporter Dongwoo Lee] In the future, plastic pyrolysis oil will be able to be used as a raw material in refining processes. Additionally, used electric vehicle (EV) batteries will be prioritized as circular resources and exempted from various waste regulations.
On the 5th, the Ministry of Environment announced the "Plan to Revitalize the Circular Economy through Regulatory Improvement and Support" containing these details. Vice Minister of Environment Yujecheol stated, "Considering the market size and future growth potential, plastics and used EV batteries are expected to lead the future circular economy market, but various regulations and systems are insufficient, posing obstacles to activation. Policy efforts to improve this are necessary."
Expansion of Plastic Waste Recycling Scope... Reduction of Waste Disposal Charges
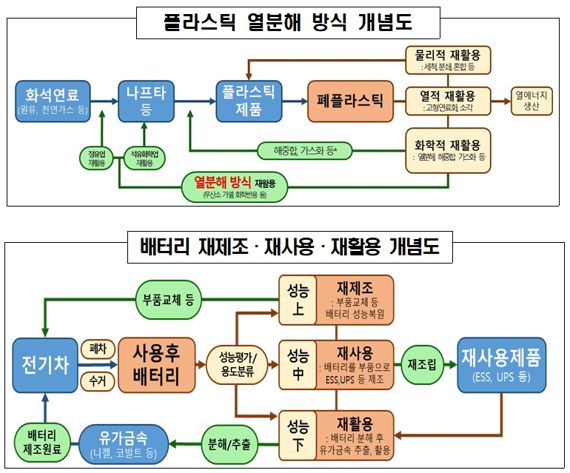
First, plastic waste that is difficult to recycle will be able to be utilized as naphtha (a petrochemical raw material) through pyrolysis. To this end, the government plans to establish recycling types and detailed standards under the Waste Management Act.
Specifically, pyrolysis oil manufacturing facilities and incineration facilities will be separated. Manufacturing facilities will be classified as recycling facilities, simplifying installation and inspection standards. For manufacturing facilities, the number of installation inspection items will be reduced by 10 and regular inspection items by 2 compared to incineration facilities.
Financial support will also be expanded. Starting next year, waste disposal charges will be reduced for plastic products recycled chemically, and efforts will be made to increase the unit price of support funds under the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) system and expand the allocation ratio. During the sorting process, the EPR support fund structure will also be reorganized to encourage high-quality sorting of vinyl-type plastics, which are pyrolysis raw materials.
To expand the pyrolysis industry ecosystem, 49.2 billion KRW will be additionally supported for research and development (R&D) to advance technology by 2025. The number of local government pyrolysis facilities, currently four, will be increased to ten by 2026. To improve the quality and supply of pyrolysis raw plastic, 4.9 billion KRW will be provided, and vinyl-type plastic sorting facilities, the main raw material, will be expanded from three to twenty.
Used EV Batteries Exempted from Waste Regulations
Used EV batteries will be prioritized as circular resources. To this end, a "Circular Resource Prior Recognition System" will be introduced, exempting them from various waste regulations. Currently, circular resource recognition is granted only for uses and methods pre-approved at the business site level.
A safety inspection system will be established for reused batteries used in manufacturing energy storage systems (ESS) for reusing used batteries. To reduce inspection burdens, only manufacturers with inspection qualifications will be allowed to conduct self-inspections. By introducing software (S/W) inspection techniques, inspection time will be shortened from the current maximum of 40 hours to 30 minutes.
To activate leasing and reuse of EV batteries, a system will be established allowing batteries to be distributed independently from EVs. A system to separately register and manage batteries during EV registration will also be created.
The entire lifecycle history of batteries?including manufacturing, registration, operation, removal, reuse, and recycling?will be managed in a public database. Part of the database will be disclosed to insurance companies and the industry. This aims to establish a foundation for independent distribution of batteries separate from vehicles, thereby promoting leasing and recycling.
By 2025, a "Resource Circulation Cluster" supporting technology development and demonstration for used battery recycling will be established in Pohang, and the number of used secondary battery industrialization centers will be increased from two to four. Plans are also underway to include battery recycled raw materials and used battery recycled and reused products in the Excellent Recycled Products (GR) certification, which receives preferential treatment in public procurement.
The Ministry of Environment expects that fostering these two industries will not only reduce waste and carbon emissions but also promote corporate investments exceeding 1 trillion KRW plus alpha.
Vice Minister Yoo said, "We will proactively respond to environmental regulations in the plastics and battery sectors newly introduced or promoted by major overseas countries to strengthen the global competitiveness of domestic industries. Through recycling used EV batteries, we will also reduce dependence on overseas critical minerals and enhance supply chain security."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.