[Asia Economy Reporter Kim Young-won] The period from the first COVID-19 infection to reinfection was found to have shortened in July compared to June.
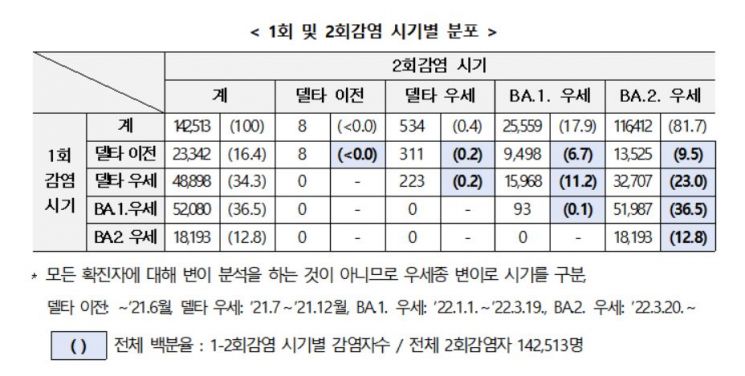
On the 11th, the Central Disease Control Headquarters announced the results of an analysis on the status of suspected reinfection cases reflecting this trend. According to the headquarters, an additional 56,679 suspected reinfection cases were reported in the third and fourth weeks of July, bringing the cumulative total to 142,513.
The average time from the initial COVID-19 infection to reinfection has shortened. In June, the average duration until reinfection among suspected cases was 229 days, but in July, it decreased by about 60 days to an average of 154 to 165 days.
By variant, the highest reinfection rate was 36.5% for those initially infected with Omicron BA.1 and then reinfected with BA.2, followed by 23.0% for initial Delta infection followed by BA.2 infection, and 11.2% for initial Delta infection followed by BA.1 infection. Approximately 80% of all suspected reinfection cases occurred during the BA.2 wave.
The distribution by timing of first and second infections was highest for ‘Omicron (BA.1) - Omicron (BA.2)’ at 36.5%, followed by ‘Delta - Omicron (BA.2)’ at 23.0%, and ‘Delta - Omicron (BA.1)’ at 11.2%.
Additionally, minors aged 17 and under and unvaccinated groups were found to be more frequently reinfected with COVID-19. Among suspected reinfection cases in July, those aged 17 and under accounted for 49.2%, nearly half. This is more than double the 23.1% proportion of those aged 17 and under among all confirmed cases since COVID-19 first appeared in Korea in January 2020.
The unvaccinated group also accounted for half of the suspected reinfection cases in July. While about 12% of the population remains unvaccinated, they represent 50% of reinfection cases.
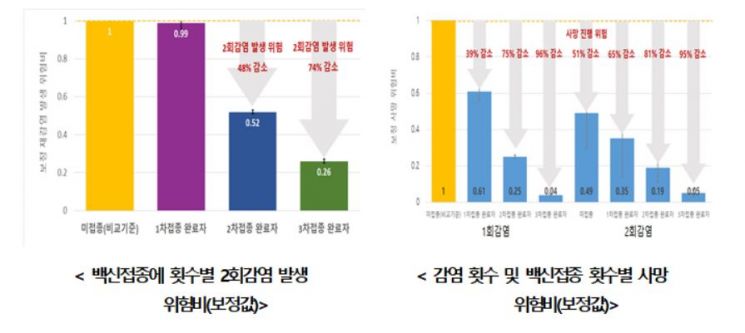
Baek Kyung-ran, Commissioner of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, introduced related research results, stating, "Vaccination is effective not only in preventing infection and severe illness but also in preventing reinfection and reducing the risk of death caused by reinfection." The risk of reinfection was 48% lower in those who completed the second dose and 74% lower in those who completed the third dose compared to the unvaccinated group. Regardless of the number of infections, the risk of death after infection was reduced by more than 95% in those who completed the third dose, and the risk of death during reinfection decreased as the number of vaccinations increased.
The Central Disease Control Headquarters pointed out that the increase in reinfections is primarily due to the rising number of cumulative confirmed cases (initial infections), the high prevalence of the highly transmissible and immune-evasive BA.5 variant, and the waning immunity from natural infection and vaccination over time.
Commissioner Baek emphasized, "With increased population movement during the summer vacation season and the upcoming weekends and Liberation Day holidays, it is a time when adherence to personal quarantine rules and protection of high-risk groups around us is especially important," and urged, "We ask the public to participate in following quarantine guidelines to ensure a safe and healthy August."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![User Who Sold Erroneously Deposited Bitcoins to Repay Debt and Fund Entertainment... What Did the Supreme Court Decide in 2021? [Legal Issue Check]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026020910431234020_1770601391.png)















