Disease Control Headquarters: Fever and Blisters Naturally Recover After 7-10 Days
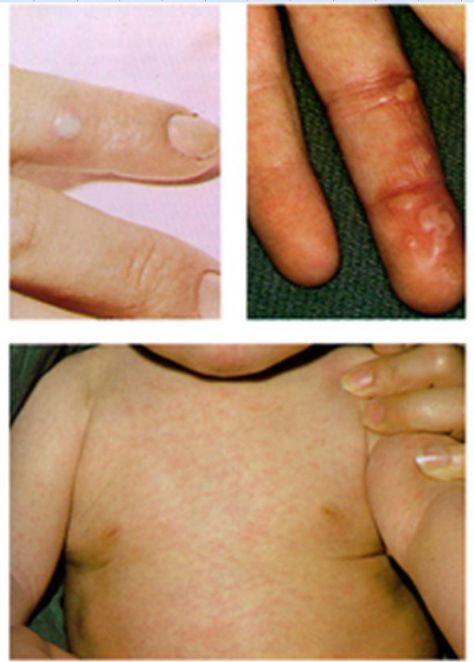
[Asia Economy Reporter Jo In-kyung] Recently, the number of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) cases among infants and young children has been increasing, prompting health authorities to urge adherence to preventive measures such as handwashing and disinfecting objects.
According to the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency on the 15th, among 211 nationwide sentinel surveillance sites, the number of suspected HFMD cases per 1,000 outpatients rose from 1.7 during June 12?18, to 2.6 during June 19?25, then to 5.4 during June 26?July 2, and further increased to 10.3 during July 3?9.
Although this is lower than the period before the COVID-19 pandemic, it is more than 10 times higher compared to the same period over the past two years, when the incidence was 0.9 cases per 1,000 outpatients.
HFMD is an infectious disease caused by infection with Coxsackievirus or Enterovirus, characterized by fever, mouth blisters, ulcers, and vesicular rash on the hands and feet.
In most cases, symptoms naturally resolve within 7 to 10 days after onset; however, complications such as meningitis, encephalitis, or paralysis may rarely occur. Therefore, if symptoms such as high fever, vomiting, or lethargy develop, prompt medical attention should be sought.
Additionally, transmission occurs through direct contact with the stool or secretions (saliva, sputum, nasal mucus, fluid from blisters, etc.) of confirmed patients, or by touching contaminated towels, toys, or objects. Therefore, in daycare centers and kindergartens, it is especially important to wash hands before and after caring for children and to carefully disinfect toys and other objects.
Considering that HFMD mainly occurs from spring to autumn, the number of cases is likely to continue for some time.
Baek Kyung-ran, Commissioner of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, stated, "Since HFMD is a common infectious disease among infants and young children, daycare centers and kindergartens where group activities take place must thoroughly maintain personal hygiene and disinfect items related to patients." She added, "If HFMD is suspected, avoid contact with others and refrain from using crowded facilities. For prevention, please maintain strict hygiene management in places where many children gather, such as swimming pools, kids cafes, and cultural centers."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
















