Carbon Dioxide Concentration Increased 2.2 Times Over the Past Decade
Annual Growth Rate 2.7 ppm Since 2019
Methane Concentration Increase Larger... 2.2 Times the 10-Year Growth Rate
[Asia Economy Reporter Han Jinju] Last year, the concentration of carbon dioxide on the Korean Peninsula reached an all-time high. In particular, methane concentration more than doubled compared to the previous year.
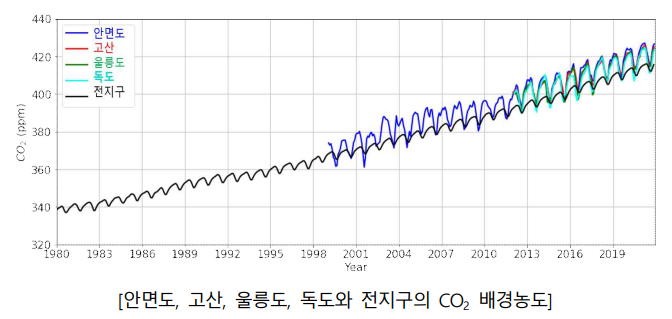
On the 12th, the Korea Meteorological Administration's National Institute of Meteorological Sciences announced in the '2021 Global Atmospheric Monitoring Report' that the background concentration of carbon dioxide at the Anmyeondo Climate Change Monitoring Station (the concentration at a location not directly affected by pollutants) was 423.1 ppm, marking the highest level since observations began in 1987. The annual increase rate has been 2.7 ppm since 2019.
The annual average background concentrations of carbon dioxide at the Gosan (421.5 ppm) and Ulleungdo (420.8 ppm) monitoring stations also increased compared to last year. Compared to 2020, Anmyeondo (420.4 ppm) rose by 2.7 ppm, Gosan (418.9 ppm) by 2.6 ppm, and Ulleungdo (417.6 ppm) by 3.2 ppm.
The global average background concentration of carbon dioxide (414.7 ppm) also increased by 2.3 ppm compared to the previous year. The global average concentration is a figure announced by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and will be finalized and released by the World Meteorological Organization this coming October.
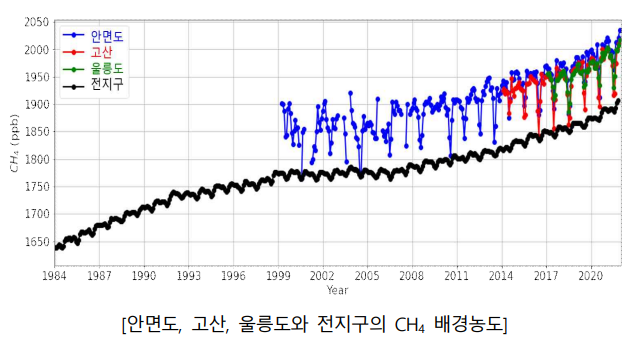
Last year, the increase in methane concentration was particularly notable. The methane background concentration at Anmyeondo also reached a record high of 2005 ppb. It rose by 22 ppb within one year, which is about 2.2 times the increase rate over the past decade (an annual increase of 10 ppb). The rapid increase in methane is a global phenomenon, not limited to the Korean Peninsula; at Mauna Loa, Hawaii, the concentration rose by 17 ppb compared to the previous year, reaching 1896 ppb.
Methane has a relatively short atmospheric lifetime of nine years, so reducing emissions can yield the fastest effects among greenhouse gases. South Korea joined the International Methane Pledge in 2021 and is making efforts to reduce methane emissions.
Due to frequent yellow dust events last year, the annual average concentration of particulate matter (PM10) rebounded. After decreasing until 2020, the frequent occurrence of yellow dust last year caused the concentration to increase by about 22% compared to the previous year (27 ㎍/㎥), reaching 33 ㎍/㎥. The number of yellow dust observation days last year was 10.8 days, four times that of the previous year (2.7 days) and 1.7 times the average year.
Yoo Heedong, Administrator of the Korea Meteorological Administration, said, "To respond to climate change and support related policies, it is important to monitor and understand climate change causative substances, including greenhouse gases." He added, "The Korea Meteorological Administration will continue to provide reliable climate information to support the successful implementation of climate change response policies."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.