Regulatory Relaxation on Graduate School Quotas in Advanced Industries like AI and Big Data Aligned with President Yoon's Policy
[Asia Economy Sejong=Reporter Kim Hyewon] The medical device software (SW) change approval system will be converted into a negative regulation system. This means that minor changes such as maintenance, repair, and security function updates of medical device software will no longer require change approval.
Also, rental and lease car companies, as well as online shopping businesses, will be able to receive separate national subsidies when purchasing electric vehicles in local governments where they have not established branches. The system for posting veterinary hospital treatment costs, which has been controversial due to excessive billing, will be made more specific by item. Regulatory relaxation measures aligned with President Yoon Seok-yeol’s emphasis on discovering talent and competitiveness in advanced industries such as semiconductors have also been introduced.
The government announced on the 13th that it held the 499th Regulatory Reform Committee meeting at the Government Seoul Office on the 10th and discussed and finalized the “Regulatory Improvement Plan for New Industry Corporate Difficulties.”
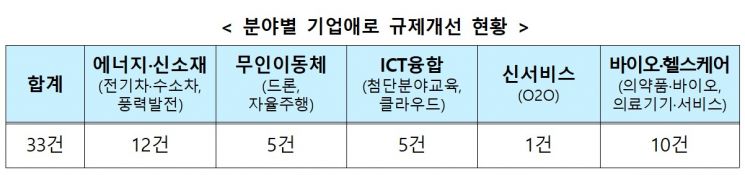
The New Industry Regulatory Innovation Committee, composed of 120 private experts, identified 33 regulations to improve in new industry sectors such as electric vehicles and hydrogen vehicles, wind power, drones and autonomous driving, ICT convergence, and bio-healthcare through 19 meetings. Among these, three have been completed, and the remaining 30 tasks will be promptly addressed through legal revisions and administrative measures.
An official from the Office for Government Policy Coordination said, “It is significant that under the Yoon Seok-yeol administration’s comprehensive regulatory innovation efforts to expand domestic and foreign corporate investment and economic growth, businesspeople, experts, and public officials have come together to swiftly prepare improvement tasks to resolve unreasonable regulations in new industry fields. We will continue to strive to resolve regulations that act as obstacles to investment in new industries in the shortest possible time.”
A notable example is the conversion of the medical device software change approval system to a negative regulation system. Medical devices require change approval when their approved items are altered, and minor changes as defined by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) notification are exempted. However, due to the nature of medical device software, maintenance, repair, and security function updates occur very frequently, but these are not included in the minor changes category, causing industry burdens such as the time required for change approval (an average of 42 days) and fees (an average of 1 million KRW). Therefore, the government decided to reduce the burden on medical device businesses and provide administrative convenience by specifying “significant changes” instead of “minor changes” and requiring change approval only in those cases, while allowing companies to self-manage changes not falling under significant changes through a negative regulation approach.
Additionally, corporations (rental and lease car companies) can now receive separate national subsidies when purchasing electric vehicles in local governments where they have not established branches. Previously, corporations operating electric vehicles nationwide could not receive separate subsidies from each local government due to difficulties in establishing branches. The payment criteria will be finalized through inter-ministerial consultation and included in next year’s electric vehicle subsidy project operation guidelines. It is estimated that about 40,000 electric vehicles will receive separate national subsidies.
In the ICT convergence sector, advanced industries such as artificial intelligence (AI) and big data have had their graduate school enrollment criteria relaxed so that graduate school quotas can increase if only the faculty recruitment rate among the four major educational conditions (faculty, teachers, school grounds, and revenue-generating basic property) is met. Previously, all four conditions had to be met. The government stated, “This will promote the training of specialized and high-level personnel in advanced industries and contribute to strengthening national competitiveness.” Joint academic programs between universities in advanced industries have been improved to allow autonomous determination of credits that can be completed at one university through inter-university agreements. Previously, the credits that could be completed at one university were limited to half of the total credits, which was a difficulty for universities in autonomously operating academic systems.
To enable timely use of the latest drone equipment, special flight safety standards will be more comprehensively defined, and approval will be granted after safety inspections by the Aviation Safety Technology Institute. Night flights of drones require special flight approval from the Minister of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, but the safety equipment and facilities required under the special flight safety standards were specifically stipulated, preventing the use of the latest equipment due to technological advancements.
For about 5,000 handling sites with low handling volumes and low risk in chemical accident prevention management plans, inspection cycles will be extended. This is to ease the operational burden on businesses by differentiating inspection cycles according to hazardous chemical handling facilities.
The installation of sterilization and crushing facilities for medical waste in hospitals will be expanded. Although medical waste generation is rapidly increasing, there are only 14 dedicated medical waste incinerators nationwide, resulting in cost burdens (about 200 billion KRW annually) due to long-distance incineration and concerns about secondary infections in case of accidents. Accordingly, the Ministry of Health and Welfare has issued an authoritative interpretation that medical waste treatment facilities such as sterilization and crushing facilities are included as auxiliary facilities (extraction treatment facilities) of medical institutions. It is expected that installation of sterilization and crushing facilities will become easier in about 140 hospitals nationwide.
Veterinary hospitals’ treatment items and treatment fee standards will also be specified. This aims to reduce consumer complaints caused by excessive treatment and overcharging. Although the posting system for veterinary hospitals was introduced through amendments to the Veterinarian Act, specific treatment items and posting methods have not yet been established. Therefore, treatment fees will be posted by item, such as basic examination, hospitalization, vaccination, tests, and interpretation fees.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![User Who Sold Erroneously Deposited Bitcoins to Repay Debt and Fund Entertainment... What Did the Supreme Court Decide in 2021? [Legal Issue Check]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026020910431234020_1770601391.png)















