Rapsus' Samsung Electronics & LG Electronics Hacking "No Vulnerabilities Found in Analysis"
[Asia Economy Reporter Lim Hye-seon] Amid increasing hacking incidents targeting domestic companies such as Samsung Electronics and LG Electronics by the hacking group Lapsus, the government announced on the 7th an analysis of cyber threat trends and step-by-step response measures.
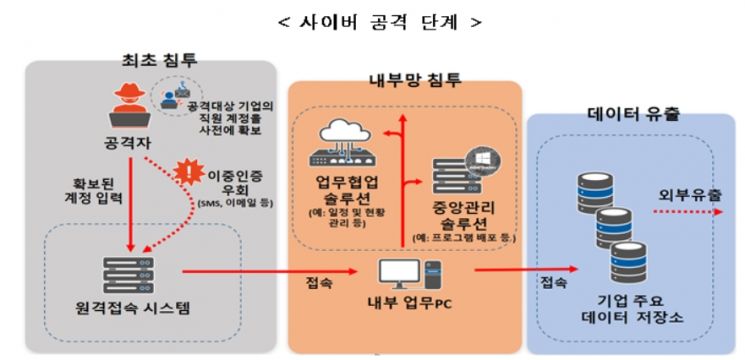
The Ministry of Science and ICT analyzed recent domestic and international breach incidents and concluded that cyberattacks from external sources can be divided into three stages: initial infiltration, internal network penetration, and data leakage.
In the initial infiltration stage, hackers purchased user accounts of the target companies from the dark web or sent malicious emails disguised as work-related messages to collect accounts and bypass additional account authentication such as one-time passwords. After infiltrating internal systems, they accessed central servers managing multiple account terminals or program management servers within the company to distribute malware for acquiring additional information. Following internal network penetration, they accessed data repositories storing product and sales-related information as well as internal employee data, secured relevant files, and exfiltrated them externally.
The Ministry of Science and ICT pointed out that breach incidents in non-face-to-face situations occurred because basic security rules or essential security policies were overlooked in favor of work efficiency.
The Ministry emphasized the need to use two-factor authentication for accessing internal systems. In particular, instead of using high-risk methods such as email authentication, it recommended using possession-based authentication like biometric authentication to reduce the possibility of external infiltration. When accessing remote work systems used for telecommuting, it is safer to apply access security policies that allow only pre-approved or designated terminals or IPs rather than permitting unrestricted access by IP or terminal.
To prevent hacking at the internal network penetration stage, it was proposed to restrict access rights to critical servers such as central management servers and patch management servers connected to multiple terminals within the company to specific administrator terminals only, and to additionally apply two-factor authentication for administrator access to internal systems. It was also added that systems to detect abnormal access attempts should be established.
To strengthen protection at the data leakage stage, it was explained that differentiated management of permissions should be applied regarding the type and importance of stored data and the scope of data access and exfiltration per user for systems storing key company materials (such as source code repositories and storage). Monitoring and blocking users attempting large-scale or repetitive data exfiltration and thoroughly managing internal server access logs were emphasized.
Kim Jeong-sam, Director of the Information Security Network Policy Division, said at a press briefing held the day before, "Hacking reports for Samsung Electronics and LG Electronics were received on March 7 and 22, respectively," adding, "Upon receiving reports, we analyze the leakage routes and leaked materials using an expert network, and so far no vulnerabilities have been found."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.