Stock Price Decline Since Last Month's Listing
Expecting Benefits from Southeast Asia's Digital Economy Growth
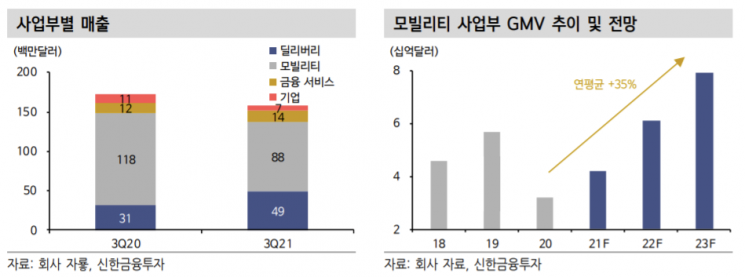
Projected Performance Growth in Mobility and Delivery Sectors
[Asia Economy Reporter Minji Lee] There is an opinion that Grab Holdings should be approached from a mid- to long-term perspective.
On the 23rd, Grab's stock price pointed to $5.6, down 22.44% since the beginning of this year. The decline in stock price is analyzed to reflect the drop in investment sentiment due to interest rate hikes and the outlook that the valuation is excessive.
Grab is a representative app in Southeast Asia. It started as a ride-sharing startup in Malaysia in 2012 but has now grown into a comprehensive platform company that has penetrated the daily lives of Southeast Asians, centered on ride-sharing, food delivery, and e-wallet services. It provides services in 8 Southeast Asian countries and 400 cities, with all core services ranking first in their respective fields. Yongmin Cho, a researcher at Shinhan Financial Investment, said, "Although it is called the Uber of Southeast Asia, considering its service portfolio, it is undervalued," adding, "Demand will continue to expand as various services can be conveniently used at affordable prices."
The most profitable business among the main business sectors is the mobility sector. Its market share in Southeast Asia reaches 75%, making it the third-largest operator globally after Uber and Didi Chuxing. The food business benefited from the COVID-19 pandemic as the food delivery market grew by 183% in 2020. Grab holds a 50% market share in the Southeast Asian online food delivery market, surpassing the combined shares of second-place Foodpanda (21%) and Gojeck (17%). The financial services sector handles fintech business, with the e-wallet market share at around 23%.
Grab's investment point is the low mobile penetration rate. All core business units are expected to benefit from the growth of the digital economy. Currently, Southeast Asia has a low smartphone penetration rate but high dependence, so the effect of expanding demand for digital services is expected to be greater. The penetration rates of Grab's core services?mobility, delivery, and e-wallet?within Southeast Asia are only 3-17%, indicating high growth potential.
The recovery in the mobility sector and the expansion of delivery are also anticipated. As COVID-19 eases, the recovery in mobility is secured, and delivery is expected to show continuous expansion. Researcher Yongmin Cho explained, "Some concerns have been raised that delivery growth will slow down due to the normalization of restaurant operating environments after the pandemic, but this is expected to be a temporary phenomenon." Delivery's GMV (Gross Merchandise Value) is expected to grow at an average annual rate of 39% through 2023.
Grab's revenue growth rates for 2022 and 2023 are 41% and 42%, respectively. Given its leading position in the rapidly growing Southeast Asian food delivery and ride-sharing markets, benefits are expected.
However, as external expansion is guaranteed, the valuation burden (7 times as of 2022) is also significant. The expected price-to-sales ratio (PSR) for this year is 6 times, indicating a heavy valuation burden. Leading U.S. mobility companies Uber and Lyft are trading at about 3 times each. Researcher Cho said, "If the pandemic prolongs, growth may be partially impaired, and Southeast Asian countries have shown vulnerability to COVID-19 due to lower vaccination rates compared to developed countries." He added, "However, all core businesses are in the early market formation stage, and revenue is expected to grow fourfold by 2025," concluding, "A premium on growth is justified, and mid- to long-term interest is necessary."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![User Who Sold Erroneously Deposited Bitcoins to Repay Debt and Fund Entertainment... What Did the Supreme Court Decide in 2021? [Legal Issue Check]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026020910431234020_1770601391.png)














