KEF, Comparison of Major Items Such as Parts and Materials Among Korea, the US, and Japan
[Asia Economy Reporter Kim Heung-soon] A survey revealed that South Korea has the highest import dependence on China among the United States, Japan, and South Korea for major items including parts and materials. Among the four key items?semiconductors, batteries, antibiotics, and rare earth elements?that the Biden administration is focusing on for supply chain restructuring, South Korea's import dependence on China ranked first among the three countries. Accordingly, there are calls for policies to reduce dependence on specific countries.
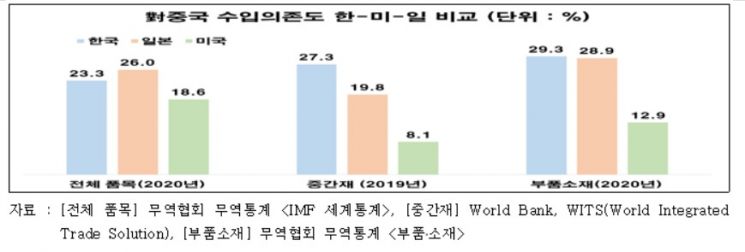
According to the Federation of Korean Industries (FKI) on the 12th, as of 2020, the global average import dependence on China for all items was 14.3%, with parts and materials at 29.3% for South Korea, 28.9% for Japan, and 12.9% for the United States. For intermediate goods, based on 2019 data, the global average was 10.4%, while among the three countries, South Korea was 27.3%, Japan 19.8%, and the United States 8.1%. The FKI explained, "The high import dependence on China for intermediate goods and parts and materials in South Korea and Japan is because South Korea, China, and Japan are connected as an economic bloc through intermediate goods trade."
Import Dependence on China Increased Most in South Korea Compared to 2017
Compared to 2017, just before the US-China trade war began, South Korea's import dependence on China for all items increased by 3.8 percentage points (p) in 2021 (January to August), while Japan's increased by only 0.1%p, and the United States' decreased by 4.2%p.
According to the World Bank's global intermediate goods trade statistics, South Korea's import dependence on China for intermediate goods increased by 0.7%p in 2019 compared to 2017, whereas Japan and the United States decreased by 0.2%p and 1.9%p, respectively.
According to the domestic Materials and Parts Comprehensive Information Network, South Korea's import dependence on China for intermediate goods rose from 27.4% in 2019 to 28.3% in 2021 (January to October). Also, as of 2020, South Korea and Japan's import dependence on China for parts and materials increased by 0.1%p and 0.9%p respectively, while the United States' decreased by 5.7%p.
South Korea Ranks First Among Three Countries in Import Dependence on China for Biden Administration's Four Key Supply Chain Items
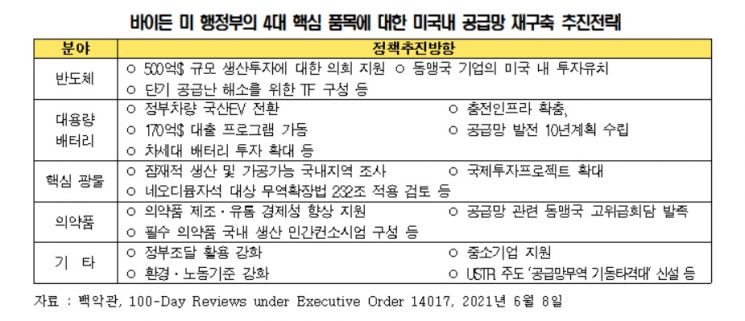
Immediately after taking office, the Biden administration has been encouraging allied companies, including those in South Korea, to participate in strengthening domestic manufacturing capabilities and reducing dependence on China for four key items: large-capacity batteries, semiconductors, critical metals and materials (rare earth elements), and pharmaceuticals and pharmaceutical raw materials. As of 2020, South Korea ranked first in import dependence on China for all four items.
According to the FKI, South Korea's import dependence on China for semiconductors was 39.5%, which is 2.2 to 6.3 times higher than that of Japan and the United States. The FKI explained that the paradoxically high import dependence on China for semiconductors in South Korea, a semiconductor powerhouse, is because domestic companies such as Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix produce a significant portion of semiconductor volumes at their Chinese local factories up to the front-end process (wafer processing) stage and then import them back to South Korea for back-end processing (wafer cutting and packaging).
For batteries (lithium-ion cells), due to environmental regulations leading to the expansion of electric vehicle adoption and the activation of renewable energy increasing demand for energy storage systems (ESS), South Korea's import dependence on China was 93.3% in 2020, 1.4 to 2.2 times higher than Japan and the United States. The FKI analyzed that the high dependence on China for batteries in South Korea is because domestic battery companies import production from their Chinese factories to meet demand that domestic supply alone cannot satisfy due to increased domestic electric vehicle sales.
South Korea's import dependence on China for pharmaceuticals and pharmaceutical raw materials (antibiotics) was 52.7%, 1.5 to 1.7 times higher than that of the United States and Japan. Additionally, South Korea's import dependence on China for rare earth elements was 52.4%, 1.2 to 1.3 times higher than Japan and the United States.
Kim Bong-man, head of international cooperation at the FKI, stated, "Global supply chain issues are being addressed not only as industrial and trade matters but also as economic security agendas. Accordingly, major countries such as the United States and the European Union (EU) are focusing on expanding domestic production facilities for key items." He added, "South Korea should also make policy and institutional efforts to reduce dependence on specific countries such as China and expand domestic production for key items."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![User Who Sold Erroneously Deposited Bitcoins to Repay Debt and Fund Entertainment... What Did the Supreme Court Decide in 2021? [Legal Issue Check]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026020910431234020_1770601391.png)














