Research Team of Lee Young-ho and Choi Dong-guk Publishes Comprehensive Paper on Latest Findings
Also Proposes Therapeutic Candidates and Development Strategies
[Asia Economy Reporter Kim Bong-su] Domestic researchers have compiled previous research results to overcome the progression of Parkinson's disease and systematized effective prevention and treatment strategies.
The Korea Basic Science Institute (KBSI) announced on the 5th that Dr. Lee Young-ho's research team from the Bio Convergence Research Division, in collaboration with Professor Choi Dong-guk's team from the Department of Biotechnology at Konkuk University, has explained the progression of Parkinson's disease in an easy-to-understand manner and systematized strategies and methods for its prevention and treatment based on this.
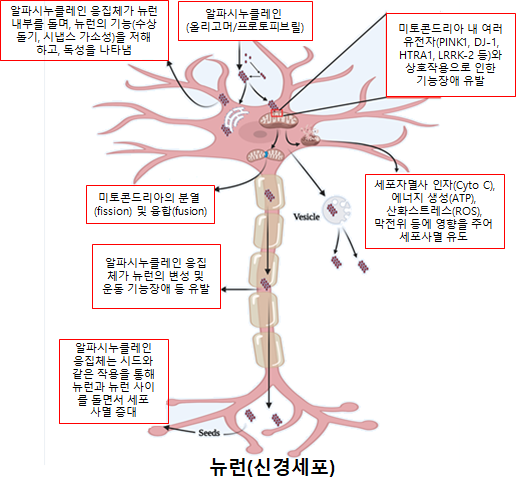
This paper comprehensively summarizes the latest research findings revealing various mechanisms related to the aggregation phenomenon of alpha-synuclein, which many experts in the field have focused on as a cause of Parkinson's disease, and mitochondrial dysfunction, an intracellular organelle. It is expected to be widely applicable in the accurate diagnosis of Parkinson's disease causes and related research fields in the future, as it presents candidate therapeutic agents and development strategies to overcome Parkinson's disease. Alpha-synuclein (α-synuclein) is an intrinsically disordered protein composed of 140 amino acids that does not have a specific structure under physiological conditions but adopts a helical structure when bound to biological membranes. Over time and with environmental changes, it forms aggregates such as oligomers or amyloid fibrils, causing various neurodegenerative diseases including Parkinson's disease and dementia.
Parkinson's disease is a representative neurodegenerative brain disorder along with stroke, characterized by the destruction of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra located in the central brainstem, leading to movement disorders and, in severe cases, progressing to dementia. However, its exact cause remains unknown. As age-related diseases have become a social issue due to population aging, about 10 million people worldwide suffer from Parkinson's disease, but the precise cause of onset is still unknown, and there is no fundamental cure.
This paper focuses on the fact that abnormal symptoms of alpha-synuclein, a protein that helps neurotransmission between brain cells, form toxic protein aggregates such as oligomers, and that these aggregates cause mitochondrial dysfunction as well as neuronal cell death, leading to Parkinson's disease.
It also addresses that alpha-synuclein not only causes mitochondrial dysfunction but also has mechanisms that help maintain mitochondrial function. The paper systematically presents effective candidates and clinical trial substances that target alpha-synuclein to maintain mitochondrial homeostasis, as well as the mechanisms and principles by which these substances regulate Parkinson's disease.
The research results were published in the January issue of the international pharmaceutical journal 'British Journal of Pharmacology'.
Dr. Lee Young-ho said, “This paper compiles the vast achievements of worldwide active research on alpha-synuclein and mitochondria-based Parkinson's disease, and we hope it will provide useful information to related researchers.” He added, “Understanding the interaction between alpha-synuclein and mitochondria is expected to be an effective idea to overcome Parkinson's disease and, further, dementia.”
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.