Increasing Dependence on Chinese Imports, Urgent Need for Countermeasures
 The Busan Chamber of Commerce and Industry announced an analysis report on the dependence of the Busan region on imports from China on the 22nd.
The Busan Chamber of Commerce and Industry announced an analysis report on the dependence of the Busan region on imports from China on the 22nd.
[Asia Economy Yeongnam Reporting Headquarters, Trainee Reporter Lee Seryeong] The Busan Chamber of Commerce and Industry announced on the 22nd the "Analysis Report on Busan Region's Dependence on Imports from China amid the Expansion of Global Supply Chain Risks."
According to data analyzed using the HS code, a classification standard commonly used in foreign trade transactions, Busan's dependence on imports from China has rapidly expanded in all aspects including scale, growth rate, and proportion compared to major import countries.
As of the cumulative total for the third quarter of this year, Busan's import amount from China was $3.37254 billion, showing a significant difference compared to major import countries such as Japan with $1.55306 billion and the United States with $955 million.
The import growth rate also recorded an outstanding figure with China increasing by 28.9% compared to the same period last year, surpassing Japan's 19.1% and the United States' 7.6%.
With the proportion of imports from China accounting for 29.7% of Busan's total imports, it was confirmed that Busan's dependence on imports from China has rather increased despite the recurring supply chain crises originating from China.
Local companies expressed concerns that excessive import dependence adversely affects the entire production process, warning that crises like last year's suspension of automobile production due to a shortage of wiring harnesses or the recent urea solution shortage could recur at any time.
Based on the HS 4-digit level, among the total 1,078 types of items currently imported in Busan, as many as 900 types are imported from China, accounting for 83.5% of Busan's total imported items.
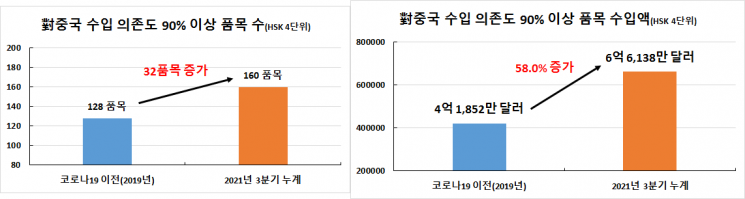
Among these, 160 items depend on China for more than 90%, and 75 items rely entirely on imports from China.
The number of items with over 90% dependence increased by 32 compared to 128 items in 2019, and the import amount for these items also rose significantly by 58%, from $418.52 million in 2019 to $661.38 million this year.
The Busan Chamber of Commerce and Industry projected that the actual growth rate is even higher considering that the data is based on import amounts up to the third quarter of this year.
The reason for the increasing dependence on imports from China despite supply chain instability is that it is difficult to overcome price competitiveness driven by labor and logistics costs, and China monopolizes major raw materials.
They warned that if dependence on essential raw materials for various industries, such as non-ferrous metals like aluminum and magnesium and organic compounds, which are entirely dependent on China, is not reduced, supply crises will recur.
The Busan Chamber of Commerce and Industry's Corporate Trend Analysis Center stated, "As we experienced difficulties due to the urea solution shortage, it is necessary to secure alternative import sources for essential items with high dependence on China and significant weight in the production process," adding, "The government and companies should prepare together by establishing an emergency stock management guide for each item."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















