Employment Rate Increased by 4.7%p Compared to Last Year
More Students Advancing to Junior Colleges Than Graduates
12-Month Retention Employment Rate Stands at 65%
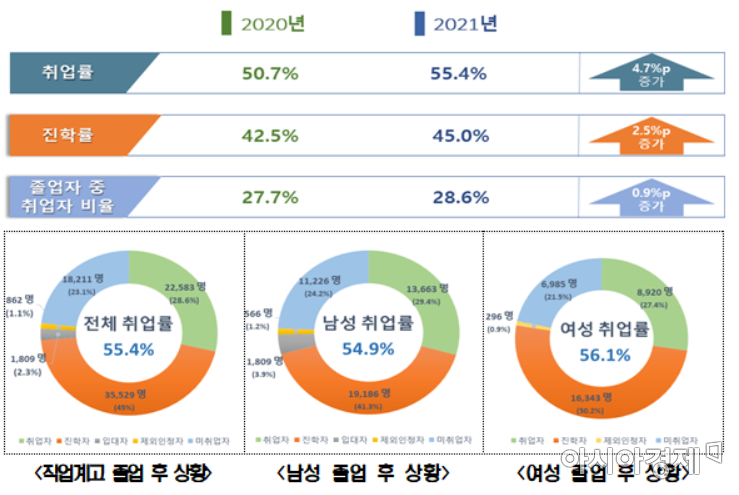
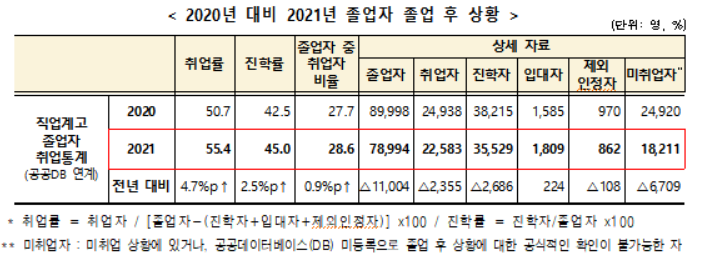
[Asia Economy Reporter Han Jinju] The employment rate of vocational high school graduates this year increased by 4.7 percentage points from last year to 55.4%.
On the 2nd, the Ministry of Education and the Korea Educational Development Institute announced the employment statistics survey for graduates from January to February this year (78,994 people) from 581 vocational high schools nationwide, and the retention employment rate survey results for 89,998 graduates from January to February last year from 576 schools.
The employment rate of vocational high school graduates refers to the proportion of employed graduates excluding those who advanced to higher education institutions, enlisted in the military, or were recognized as unable to participate in economic activities. The proportion of employed persons among all graduates this year is 28.6%.
The advancement rate to higher education among all graduates is 45%. The number of students advancing to higher education (35,529) is 1.57 times higher than the number of employed graduates (22,583). Among this year's higher education entrants, 66.8% enrolled in junior colleges.
The Ministry of Education analyzed, "Due to changes in industrial structure and the development of information technology (IT), high school graduate jobs have decreased while demand for personnel with junior college degrees or higher has expanded, increasing the demand for advanced vocational education."
The 'secondary retention employment rate,' which is the rate of maintaining employment qualifications for 12 months from last April, was only 65%. This is lower than the primary retention employment rate (77.3%) based on 6 months, which was calculated in March.
By school type, the employment rate is highest at Meister High Schools (industry demand customized) at 75%, followed by Specialized High Schools at 53.4%, and general high school vocational classes at 35.9%. The employment rate by gender is 54.9% for males and 56.1% for females.
An official from the Ministry of Education explained, "Meister High Schools involve industries from the curriculum planning stage, have high utilization of customized programs and industry-academic cooperative teachers. Since many fields that can be connected to industries are designated, the employment rate is high, and students who advance to higher education also tend to have a strong will to find employment."
By school location, Gyeongbuk (65.1%), Daegu (61.8%), and Daejeon (58.9%) had the highest employment rates. The employment rate of schools located in the metropolitan area is 53.9%, while schools outside the metropolitan area have an employment rate of 56.5%.
By work region, 55.5% of employed graduates worked at companies located in the metropolitan area, and 44.5% worked outside the metropolitan area. The proportion of employment within the city or province where the school is located is 61.9%, and employment in other cities or provinces is 38.1%.
By the curriculum group of the students' departments, employment rates were high in Electrical and Electronics (63.6%), Mechanical (63%), and Chemical Industry (61.6%). By industry type of insured workers, manufacturing (47.7%), wholesale and retail trade (8.8%), and accommodation and food service activities (5.3%) followed.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.