[Asia Economy Reporter Ji-hwan Park] The audit item that external auditors paid the most attention to during the audit process last year was related to 'revenue recognition and asset impairment.'
According to the analysis and implications of the 2020 audit report key audit matters (KAM) disclosure status announced by the Financial Supervisory Service on the 30th, the average number of KAM disclosures per company among all listed companies subject to KAM (excluding KONEX) was 1.09 for 2,212 companies last year. This level was analyzed to be not as high compared to the average number of KAMs of 3.6 for listed companies in major overseas countries such as Europe. Due to the expansion of the scope of application, the average number of KAMs slightly decreased from 1.18 the previous year. External auditors select the most significant matters communicated with the governance body as KAMs and disclose the reasons for selecting KAMs and audit methods in the audit report to enhance the understanding of information users.
Looking at the number of KAMs by auditor size, it was found that companies audited by large accounting firms had more KAMs. The average number of KAMs was 1.21 for large firms, slightly higher than 1.03 for mid-sized and 1.04 for small firms.
By industry, the average number of KAMs exceeded the industry average (1.09) in construction (1.13), wholesale and retail trade (1.13), and manufacturing (1.10). The number of KAMs increased with asset size: less than 100 billion KRW (0.97), 100 billion to 500 billion KRW (1.10), 500 billion to 2 trillion KRW (1.22), and over 2 trillion KRW (1.46). Additionally, KOSPI-listed companies had slightly more KAMs (1.21) than KOSDAQ-listed companies (1.02).
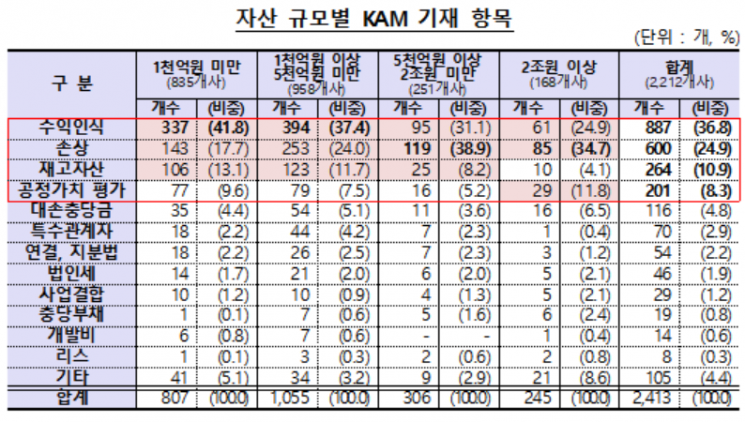
The KAM disclosure items mainly included areas with high audit risk or those involving management judgment, such as revenue recognition (36.8%), impairment (24.9%), inventory (10.9%), and fair value measurement (8.3%). Excluding the commonly disclosed revenue recognition and impairment items, companies with assets over 2 trillion KRW showed a higher proportion of fair value measurement, while those with assets under 2 trillion KRW had a higher proportion of inventory items. The Financial Supervisory Service explained that this is mainly because most listed companies operating in the financial industry, where fair value measurement is a major issue, have total assets exceeding 2 trillion KRW.
Manufacturing, service, and construction industries showed a high proportion of KAM disclosures in the order of revenue recognition and impairment. In particular, construction had a significantly high proportion of revenue recognition disclosures (88.3%) due to the industry's characteristics (order-based industry). Wholesale and retail trade showed a higher proportion of impairment followed by revenue recognition. Like manufacturing, the proportion of inventory disclosures was also high. The financial industry, with a high proportion of financial assets and liabilities, showed a high proportion of KAM disclosures in the order of impairment and fair value.
The Financial Supervisory Service stated that while the overall KAM disclosure status was generally good, some deficiencies such as non-disclosure and general or abstract descriptions were also found. A Financial Supervisory Service official said, "Auditors are mainly disclosing KAMs for items with high audit risk or those involving management judgment, and the identified deficiencies are minimal, indicating that the key audit matter system is relatively well established."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.