Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology
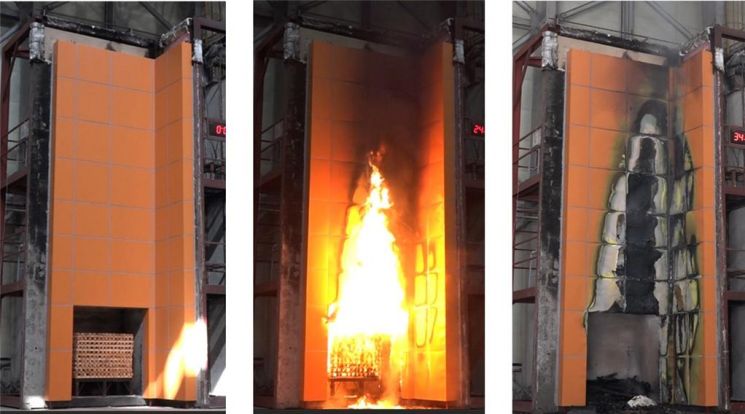 A new concept building exterior wall construction method developed by the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology. Fire resistance tests conducted according to the standards of the UK Building Research Establishment for international certification showed that it withstood 21 minutes, demonstrating performance 140% better than the international standard of 15 minutes.
A new concept building exterior wall construction method developed by the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology. Fire resistance tests conducted according to the standards of the UK Building Research Establishment for international certification showed that it withstood 21 minutes, demonstrating performance 140% better than the international standard of 15 minutes.
[Asia Economy Reporter Kim Bong-su] The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology announced on the 30th that it has developed a world-class building exterior wall construction method that offers excellent insulation performance and strong fire resistance.
As insulation performance standards for buildings are increasingly strengthened to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, construction using exterior insulation methods such as Dryvit (a method where combustible insulation materials are installed on building exterior walls and then covered with mesh and mortar; easy to construct but highly vulnerable to fire) is on the rise. Metal composite panels, which are easy to install and have an attractive appearance, are commonly used as exterior wall construction methods for high-rise and super high-rise buildings.
However, in existing methods, heat loss frequently occurs due to the heat bridge phenomenon, where warm indoor air or heat escapes through the building structure because of the space between the building exterior wall and the finishing material. Due to the stack effect, where strong air currents inside high-rise buildings rise or descend vertically, fires in high-rise buildings have rapidly spread vertically.
A representative case is the 33-story residential-commercial complex apartment in Ulsan that caught fire last October. Although non-combustible insulation materials that do not burn were used and the exterior was finished with metal composite panels, the fire that started on the 3rd floor quickly spread to the top.
Dr. Lee Taewon’s research team at the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology improved this issue by constructing unit metal composite panel modules with attached insulation materials, and reinforcing the hollow space (air gap inside the building wall created during construction) at the joints between these modules with insulating and fire-resistant materials. By filling the previously empty space with materials that provide insulation and fire resistance, this new building exterior wall structure and method can effectively reduce heat loss and fundamentally block fire spread. It is expected to achieve both energy savings and improved fire safety performance simultaneously.
Performance verification results confirmed insulation performance at the level of 0.147 W/㎡·K, surpassing the residential building insulation standard (thermal transmittance 0.15 W/㎡·K) for domestic central region 1 areas such as Yeoncheon and Paju. Full-scale fire experiments were conducted at their own research institute to verify fire spread prevention performance. The fire spread delay time was confirmed to be more than four times longer, increasing from 5 minutes in existing Dryvit or aluminum composite panel methods without filled hollow spaces to 23 minutes.
In particular, a cross-evaluation was conducted with the UK Building Research Establishment (BRE), the only institution in the world that performs full-scale fire safety tests on building exterior wall systems under the BS 8414 Test certification. The developed method exceeded the international standard of 15 minutes, achieving 21 minutes, confirming its performance with the international certification body.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
















