Statistics Korea Announces Regional Employment Survey Results for the First Half of the Year
 After the Chuseok holiday, on the first working day, the 23rd, citizens returning to their daily lives are hurrying on their way to work on the streets of Gwanghwamun, Seoul. Photo by Hyunmin Kim kimhyun81@
After the Chuseok holiday, on the first working day, the 23rd, citizens returning to their daily lives are hurrying on their way to work on the streets of Gwanghwamun, Seoul. Photo by Hyunmin Kim kimhyun81@
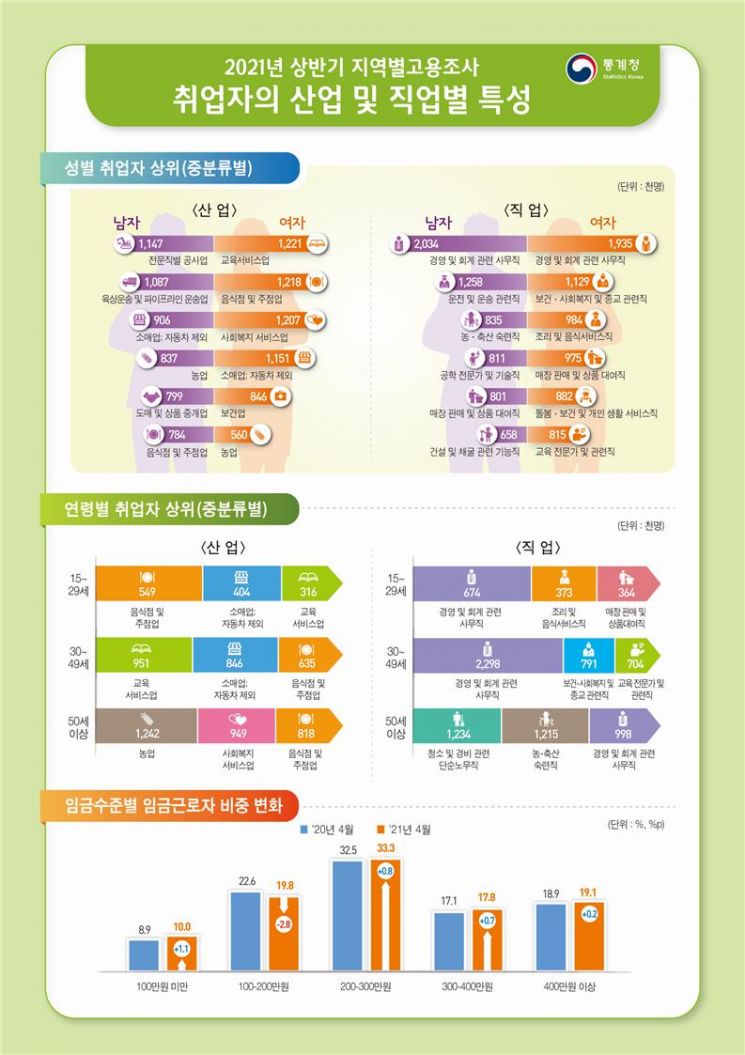
[Sejong=Asia Economy Reporter Kim Hyunjung] It has been revealed that 6.15 million wage workers, accounting for about 30% of the total, earn less than 2 million won per month. Among those working in the accommodation and food service industry, 27% earned less than 1 million won per month.
According to the '2021 First Half Regional Employment Survey - Characteristics of Employed Persons by Industry and Occupation' released by Statistics Korea on the 19th, among 2.647 million wage workers as of April this year, 2.056 million (10.0%) earned less than 1 million won per month, and 4.097 million (19.8%) earned between 1 million and less than 2 million won. This includes part-time and temporary workers, meaning that about 3 out of 10 wage workers, totaling 6.153 million (29.8%), earned less than 2 million won per month.
The largest proportion was those earning between 2 million and less than 3 million won, with 6.875 million (33.3%). Those earning between 3 million and less than 4 million won accounted for 3.666 million (17.8%), and those earning 4 million won or more were 3.952 million (19.1%). Compared to the same period last year, the proportion of low-wage workers earning less than 1 million won increased by 1.1 percentage points, and the proportion of high-wage workers earning 4 million won or more also rose by 0.2 percentage points. Conversely, the proportion of workers earning between 1 million and less than 2 million won decreased by 2.8 percentage points.
In the accommodation and food service industry, the proportion of low-wage workers earning less than 1 million won per month was high at 27.5%. Using 2 million won as the threshold, 62.1% of wage workers in this industry earned less than 2 million won. Among those earning between 1 million and less than 2 million won, agriculture, forestry, and fisheries had the highest proportion at 37.9%, while those earning between 2 million and less than 3 million won were most prevalent in business facility management, business support, and rental services at 41.2%. By occupation, among wage workers earning less than 1 million won, simple labor workers accounted for the highest proportion at 28.2%, while managers made up the majority (80.0%) of those earning 4 million won or more.
Conversely, high-wage workers earning 4 million won or more were predominantly found in finance and insurance (41.3%), professional scientific and technical services (40.8%), and information and communication industries (38.8%).
When dividing all employed persons, including non-wage workers (27.214 million), by detailed industry classification (232 categories), restaurant workers were the largest group at 1.613 million (5.9%). By medium industry classification (77 categories), excluding automobile retail, wholesale and retail trade had 2.057 million (7.6%), restaurant and bar industry had 2.002 million (7.4%), and education services had 1.825 million (6.7%) workers, in that order.
Compared to the same period last year, social welfare service employment increased by 179,000, showing the largest growth. Despite the spread of COVID-19, employment in the restaurant and bar industry also increased by 68,000.
By age group, among youth aged 15-29, restaurant and bar employment was the highest at 549,000. For those aged 30-49, education services had the most workers at 951,000, and for those aged 50 and above, agriculture had the highest employment at 1.242 million. By education level, those with middle school education or less were mostly employed in agriculture (836,000), high school graduates in restaurant and bar industry (1.106 million), and college graduates or higher in education services (1.5 million).
Looking at employment by occupational status and major industry classification (21 categories), among regular wage workers, manufacturing had the highest proportion at 23.8%, while temporary and daily workers were mostly distributed in construction (13.9%) and accommodation and food service industries (12.8%). By detailed occupation classification, the most common jobs were management-related clerks (2.32 million, 8.5%), store sales workers (1.745 million, 6.4%), and crop cultivation workers (1.228 million, 4.5%).
Among male workers, management-related clerks were the most common, followed by automobile drivers and store sales workers. Female workers were mostly employed as store sales workers, management-related clerks, and cleaners and environmental workers.
By medium occupation classification, management and accounting clerical workers were the largest group at 3.97 million (14.6%). Compared to the same period last year, the number of employed persons increased most significantly in simple labor jobs related to cleaning and security (1.379 million, 5.1%), with an increase of 202,000.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.