Professor Sanghyun Park's DGIST Team Develops Deep Learning Model for Automatic Classification of Bacterial Pneumonia
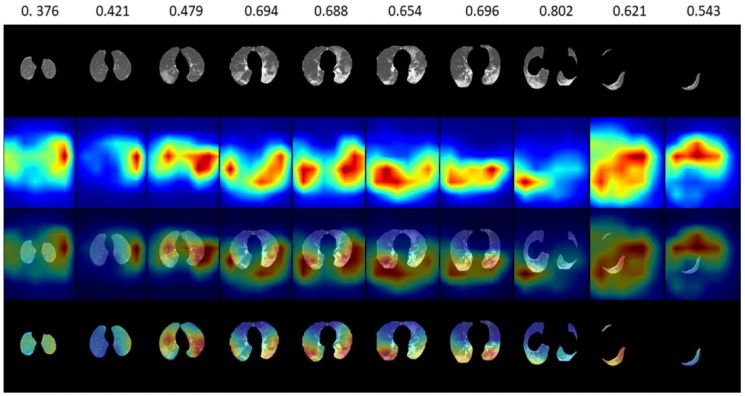 The first line represents the attention values, the second line shows the input CT slices, the third line visualizes the attention regions, the fourth line displays a visualization combining the original image and the attention regions, and the fifth line visualizes the attention regions limited to the lung area.
The first line represents the attention values, the second line shows the input CT slices, the third line visualizes the attention regions, the fourth line displays a visualization combining the original image and the attention regions, and the fifth line visualizes the attention regions limited to the lung area.
[Asia Economy Reporter Kim Bong-su] A system that accurately distinguishes between pneumonia caused by COVID-19 and bacterial pneumonia using artificial intelligence (AI) has been developed.
Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) announced on the 30th that Professor Park Sang-hyun's robotics team collaborated with Professor Ahn Jun-hong's team at Yeungnam University Hospital to develop a deep learning model that can automatically classify bacterial pneumonia and COVID-19 patients, which are difficult to distinguish by identifying key lesions in CT images. This is expected to make a groundbreaking contribution not only to pneumonia caused by COVID-19 but also to the diagnosis of various types of pneumonia in the future.
When pneumonia worsens, doctors examine the patient's condition through CT images. Although research on applying deep learning technology for accurate CT image analysis is active, it is difficult to precisely distinguish COVID-19 pneumonia from bacterial pneumonia. The differences are subtle, making it challenging to check and classify lesions one by one in three-dimensional images. Even recently developed deep learning models that have shown good performance in various fields have had limited effectiveness.
The research team newly proposed a model that allows AI to automatically focus on key lesions within CT images and perform classification without having to check each lesion individually in three-dimensional images. They developed a new deep learning model using Multiple Instance Learning, which is used for problems that make final decisions by comprehensively considering multiple cases.
To improve the model's performance, an ‘Attention module’ was integrated to focus intensively on the locations of pneumonia lesions in CT images. Additionally, by using contrastive learning based on unsupervised learning, the feature extraction performance for each patient was maximized, significantly enhancing the classification performance of the newly developed model.
The newly developed deep learning model showed a final accuracy of 98.6% in diagnosing COVID-19, greatly surpassing the performance of other previously proposed Multiple Instance Learning methods.
Professor Park said, “The model developed through this research not only significantly improved COVID-19 diagnostic performance but also showed great improvements in the field of Multiple Instance Learning AI. It is expected to contribute to overcoming the pandemic, and if related technologies are further improved in the future, it could be applied to the diagnosis of various types of pneumonia.”
The results of this study were published last month in the international academic journal related to medical image analysis, ‘Medical Image Analysis.’
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















