DGIST Professor Gwak Jeongho's Team in Information and Communication Convergence Develops 6G-Optimized 'Integrated Computing and Network Chaining Technology'
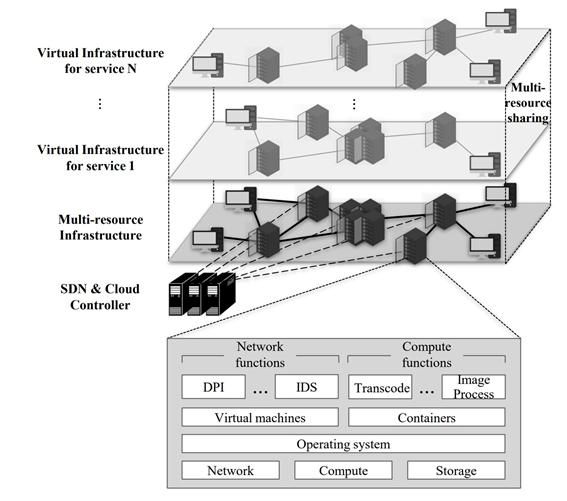 The above illustration explains how various services that utilize network functions and computing functions, along with EKD services, are embedded into the virtual infrastructure.
The above illustration explains how various services that utilize network functions and computing functions, along with EKD services, are embedded into the virtual infrastructure.
[Asia Economy Reporter Kim Bong-su] A fundamental technology that can efficiently mobilize computing and network resources for next-generation ultra-high-speed mobile communication technology (6G) services has been developed by domestic researchers.
The Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) announced on the 6th that Professor Gwak Jeong-ho's team from the Department of Information and Communication Convergence developed an "Integrated Computing and Network Chaining Technology" optimized for 6G services. The developed technology simultaneously considers computing and network resources for processing, demonstrating high Quality of Experience (QoE) in practical use, enabling the application of various killer applications essential for processing massive amounts of data in the upcoming 6G era.
Currently, network chaining technology applied to mobile applications only considers network communication traffic. However, VR/AR services and hologram graphic services utilizing the 6G network to be developed in the future are expected to actively use technology where mobile devices process enormous amounts of data together with cloud computing servers on the network.
The research team predicted that existing network architectures considering only network resources would have limitations in applying such technologies. They proposed a framework that considers multiple computing resources and network communication traffic resources available across the entire network in real-time and efficiently controls their use, along with an algorithm called ‘DualRMR’.
The framework and algorithm developed by the research team determine network resource allocation and routing based on the amount and level of data that applications used on mobile devices need to process. For example, cloud offloading services requiring many processing cycles can connect the mobile device to the server with the most computing resources at the necessary time.
Simulations conducted on the actual U.S. internet network confirmed that the developed DualRMR algorithm reduced system costs by an average of 21.7% compared to the existing usability maximization algorithm while maintaining the same throughput and fairness performance. Compared to the existing system cost minimization algorithm, it showed 73.3% higher throughput at the same system cost.
Professor Gwak said, “This research is a technology suitable for optimizing the performance and system resources of next-generation applications that dynamically utilize network and computing resources according to changes in time and space,” adding, “The goal is to apply it to various applications that dynamically utilize computing resources, such as remote medical services and hologram graphic services in the 6G era.”
The research results were published online on July 7 in the international journal ‘IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing.’
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)










