Analysis of University Information Disclosure Results: General High School Graduates Decreased from 74.8% to 73.4%
Specialized High Schools Increased from 5.1% to 5.9%, GED Holders from 1.7% to 2.1%
9,129 Admissions Officers Participated in College Entrance Exams, 13% Were Full-Time
Last Year, General Universities' Remote Classes Increased by 2710%, with 12.36 Million Enrolled Students
[Asia Economy Reporter Han Jinju] The proportion of freshmen admitted to general universities through opportunity-balanced selection from general high schools slightly decreased this year. This is due to an increase in admissions from specialized high schools and GED holders.
On the 30th, the Ministry of Education and the Korea Council for University Education announced the results of the "June 2021 University Information Disclosure Analysis." The data analyzed 195 four-year general and education universities and 133 junior colleges.
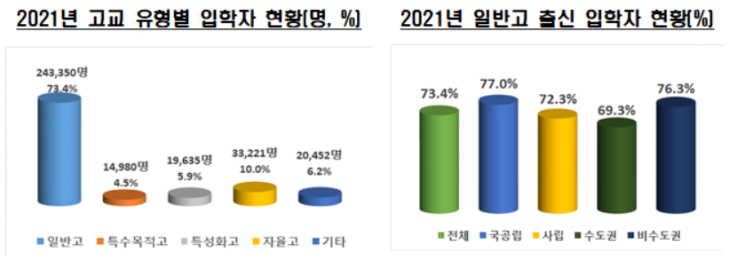
In the 2021 academic year, freshmen admitted through opportunity-balanced selection to general and education universities came from the following high school backgrounds: general high schools 73.4% (243,350 students), special-purpose high schools 4.5% (14,980 students), specialized high schools 5.9% (19,635 students), autonomous high schools 10.0% (33,221 students), and others 6.2% (20,452 students).
The proportion of students from general high schools decreased by 1.4 percentage points compared to the previous year. This was influenced by an increase in the proportion of specialized high school graduates and GED holders entering universities. Specialized high schools accounted for 5.9%, up 0.8 percentage points from the previous year, and GED holders increased by 0.4 percentage points to 2.1%. The overall decrease in the proportion of general high school students among all high school students also had an impact.
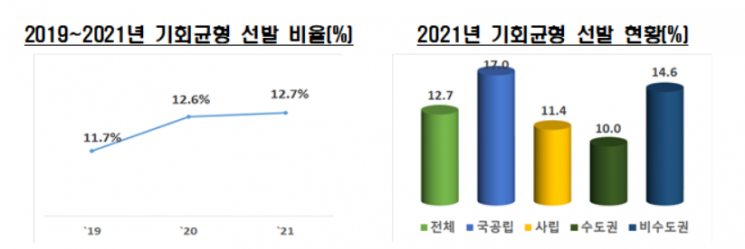
The proportion of freshmen admitted through opportunity-balanced selection increased by 0.1 percentage points to 12.7% compared to 2020. Opportunity-balanced selection is a special admission process outside the quota that provides equitable opportunities to students from rural areas, graduates of specialized high schools, recipients of basic living subsidies, and others.
The rate of opportunity-balanced selection at national and public universities was 17.0%, 5.6 percentage points higher than private universities (11.4%), and non-metropolitan universities (14.6%) had a rate 4.6 percentage points higher than metropolitan universities (10.0%). The proportion of general high school graduates at national and public universities was 77.0%, 4.7 percentage points higher than private universities (72.3%), and non-metropolitan universities had a higher rate (76.3%) than metropolitan universities (69.3%).
Looking at the high school backgrounds of junior college freshmen: general high schools 59.8% (85,865 students), special-purpose high schools 1.5% (2,153 students), specialized high schools 22.6% (32,497 students), autonomous high schools 4.6% (6,637 students), and others 11.5% (16,454 students).
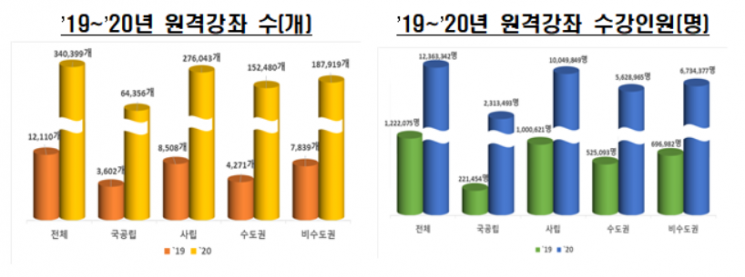
With the increase in non-face-to-face classes due to COVID-19, the number of remote lectures at general universities last year was 340,399, a 2710.9% increase compared to the previous year. The number of remote lecture attendees was 12,363,342, an increase of 911.7% year-on-year. For junior colleges, the number of remote lectures was 89,533, up 6667.4%, and the number of attendees was 3,401,596, up 2190.3% compared to the previous year.
In November 2019, universities began disclosing new data on the status of full-time admissions officers and the number of document evaluations per evaluator in student record comprehensive screening to ensure fairness in the admissions process, following the "Measures to Strengthen Fairness in University Admissions."
In the 2021 academic year, 9,129 admissions officers participated in the admissions process, of whom 1,198 were full-time. Among full-time admissions officers, 68.1% were regular employees, including indefinite-term contract workers. The average number of document evaluations per evaluator was 171.6. A total of 8,282 people participated in student record comprehensive screening document evaluations, assessing 1,421,561 documents.
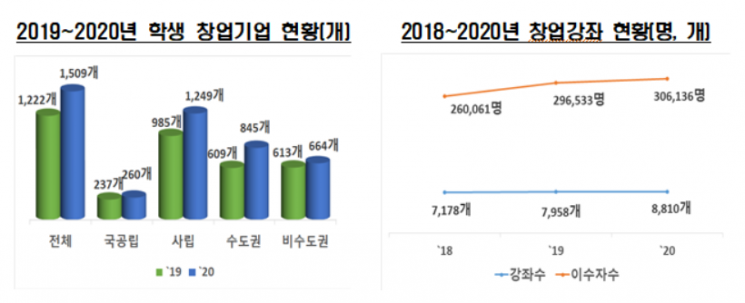
Supported by a social atmosphere encouraging entrepreneurship, the number of new student startup companies increased significantly. Last year, the number of student startup companies at general universities was 1,509, a 23.5% increase from the previous year. The number of entrepreneurship courses was 8,810, up 10.7%, and the number of students completing entrepreneurship courses was 306,136, up 3.2%.
Technology transfers numbered 5,030 last year, a 7.5% increase from the previous year. Technology transfer income was 87.4 billion KRW, a 0.6% decrease year-on-year. Income per technology transfer case was 17.37 million KRW, down 7.5% compared to the previous year.
Meanwhile, the number of contract departments operated this year was 234, down 3.3% from the previous year, and the number of students was 7,859, a 1.3% decrease. Contract departments operate curricula based on industry demands and are divided into employment-condition types and re-education types. Employment-condition contract departments numbered 53, a 51.4% increase, while re-education contract departments numbered 181, a 12.6% decrease.
The "customized curriculum," which integrates industry demand with preferential hiring conditions, numbered 401 last year, a 2.7% decrease from the previous year. The number of students participating in customized curricula was 15,885, down 1.8%.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.

![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)














