Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology Develops Perovskite Quantum Dot Material with Improved Air and Chemical Stability
High Color Purity and Luminescence Efficiency Highlighted as Next-Generation Display
[Asia Economy Reporter Kim Bong-su] A next-generation display material with enhanced durability and higher luminous efficiency has been developed.
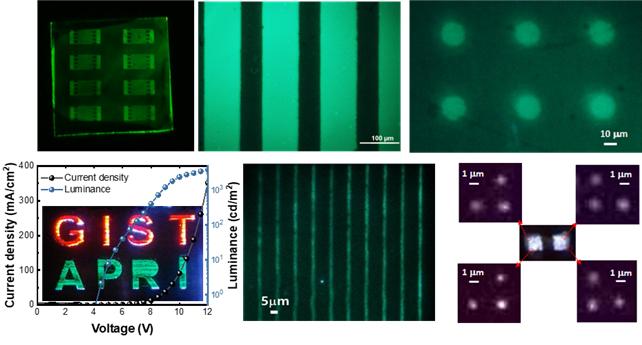
The Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) announced on the 10th that Dr. Chang-Yeol Lee's research team at the Advanced Photonics Research Institute (APRI) succeeded in developing perovskite quantum dot materials with significantly improved atmospheric and chemical stability by suppressing surface crystal defect formation through the addition of photo-initiators, photo-crosslinkers, and ligands. They also realized a white electroluminescent device with a resolution of 1 micrometer (um) using an inkjet printing process.
A photo-initiator is a substance that forms radicals under ultraviolet (UV) or visible light to facilitate efficient crosslinking reactions of photo-crosslinking materials (polymers or ligands). Photo-crosslinking is a chemical reaction that hardens upon exposure to light, and ligands refer to surfactants with various carbon chain lengths. They attach to the surface of quantum dots to enable stable dispersion of the quantum dots in solution.
Perovskite quantum dot materials have recently attracted attention as next-generation display materials that can replace organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) due to their high luminous efficiency and high color purity.
The problem is that due to their ionic bonding characteristics, they easily decompose under moisture, oxygen, and polar solvents, making it difficult to maintain luminous efficiency and color purity over a long period. There is also the disadvantage that applying photolithography semiconductor processes for high-resolution display implementation is challenging.
The research team improved the stability of perovskite quantum dot solutions and thin films by adding photo-initiators and photo-crosslinking ligands to perovskite quantum dot solutions synthesized via precipitation methods. The added photo-initiators and photo-crosslinking ligands suppressed the formation of surface defects that degrade the luminous properties and structural stability of perovskite quantum dot materials by regulating the ligand equilibrium state, including ligand dissociation and bonding.
Dr. Chang-Yeol Lee of GIST explained, “The development of high-efficiency perovskite quantum dot materials with long-term stability secured through the introduction of a newly developed photo-crosslinking ligand system is an important step forward for the commercialization of next-generation displays using perovskite quantum dot materials.”
The research results were published online on the 3rd of last month in the international materials science journal ‘Advanced Materials.’
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.