Exports -5.4%, Employment Rate -0.8%... Prices Up 0.5%
Manufacturing Up 0.4% Due to Strong Semiconductor and Machinery Equipment Performance
[Sejong=Asia Economy Reporter Moon Chaeseok] Last year, due to the impact of COVID-19, service industry production decreased nationwide except in Seoul. Exports and employment also declined in most regions across the country, while prices rose.
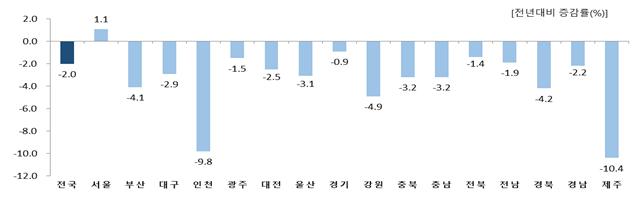
According to the '2020 Q4 and Annual Regional Economic Trends' released by Statistics Korea on the 22nd, service industry production last year decreased by 2% nationwide compared to the previous year on average.
Excluding Seoul (1.1%), the rest of the country showed a declining trend, with Jeju (-10.4%), Incheon (-9.8%), and Gangwon (-4.9%) showing the highest rates of decrease.
Statistics Korea explained, "In Jeju, Incheon, and Gangwon, production in accommodation and food services, transportation and warehousing, and arts, sports, and leisure sectors decreased, leading to a decline in service industry production."
In other words, industries involving a lot of face-to-face contact were hit hard by COVID-19, resulting in reduced production.
Seoul (1.1%) saw an increase in production centered on finance and insurance, and real estate industries.
Retail sales declined in Jeju (-26.9%), Seoul (-9.0%), and Incheon (-8.5%) due to sluggish duty-free shops and specialty retail stores.
Jeonnam (4.1%), Gyeongnam (1.9%), and Chungnam (1.6%) saw increases as sales rose in passenger car and fuel retail stores, supermarkets, and convenience stores.
Despite the decline in service industry production and retail sales, consumer prices rose by 0.5% nationwide compared to the previous year. All 17 metropolitan cities and provinces experienced increases.
Regions where last year's consumer price inflation rate was higher than the national average (0.5%) included Incheon (0.8%), Chungnam (0.7%), Jeonnam (0.7%), Seoul (0.6%), Gyeonggi (0.6%), Gangwon (0.6%), and Gyeongnam (0.6%), totaling seven areas.
In particular, Incheon, Chungnam, and Jeonnam saw higher-than-average increases due to rising prices of agricultural products and personal services.
Last year, the nationwide average industrial production increased by 0.4% compared to the previous year. Among the 17 metropolitan cities and provinces, 14 experienced declines, while 3 saw increases.
Gyeonggi (9%), Sejong (7.6%), and Gwangju (0.7%) had the highest growth rates. This was influenced by increased production of electronic components, semiconductors, and electrical equipment.
On the other hand, Seoul (-14.7%), Daegu (-11.3%), and Gyeongnam (-6.9%) saw decreases due to reduced production of clothing and fur, machinery equipment, and other transportation equipment.
Last year, exports (based on customs clearance) decreased by 5.4% nationwide. Twelve metropolitan cities and provinces experienced declines compared to the previous year.
In particular, exports of other petroleum products and passenger cars decreased sharply in Ulsan (-19.3%), Busan (-18.8%), and Jeonnam (-16.9%).
Daegu (-16.4%) and Jeonbuk (-10.6%) also showed double-digit decline rates.
Last year, nationwide construction orders increased by 15.8% compared to the previous year.
Ulsan (117.7%), Busan (97.3%), and Gyeongbuk (95.1%) saw large increases due to growth in orders for housing, offices and stores, and ports and airports.
Conversely, Jeju (-34.1%), Incheon (-21.9%), and Gwangju (-16.9%) experienced significant decreases in construction orders, mainly in housing, offices, and stores.
Last year, the employment rate nationwide averaged 60.1%, down 0.8 percentage points from the previous year. This was influenced by lower employment rates among people in their 20s, 40s, and 50s.
Gyeonggi (-1.6 percentage points), Gangwon (-1.5 percentage points), and Jeju (-1.3 percentage points) experienced the largest drops in employment rates.
The unemployment rate rose in Busan (0.5 percentage points), Seoul (0.2 percentage points), Daegu (0.2 percentage points), Incheon (0.2 percentage points), Gwangju (0.2 percentage points), Daejeon (0.2 percentage points), and Sejong (0.1 percentage points).
Ulsan recorded the same figure as the previous year.
In terms of population movement last year, regions with net inflows included Gyeonggi (168,373 people), Sejong (13,025 people), and Gangwon (5,457 people), among six areas.
Eleven regions, including Seoul (-64,850 people), Gyeongbuk (-16,978 people), and Daegu (-16,835 people), experienced net outflows.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.