Average CEO Compensation Over 500 Million KRW in Insurance Companies
CEO Salary Highest and Lowest Amounts Differ by 3 to 5 Times
"Reduce Base Salary Proportion and Increase Performance-Based Pay Proportion"
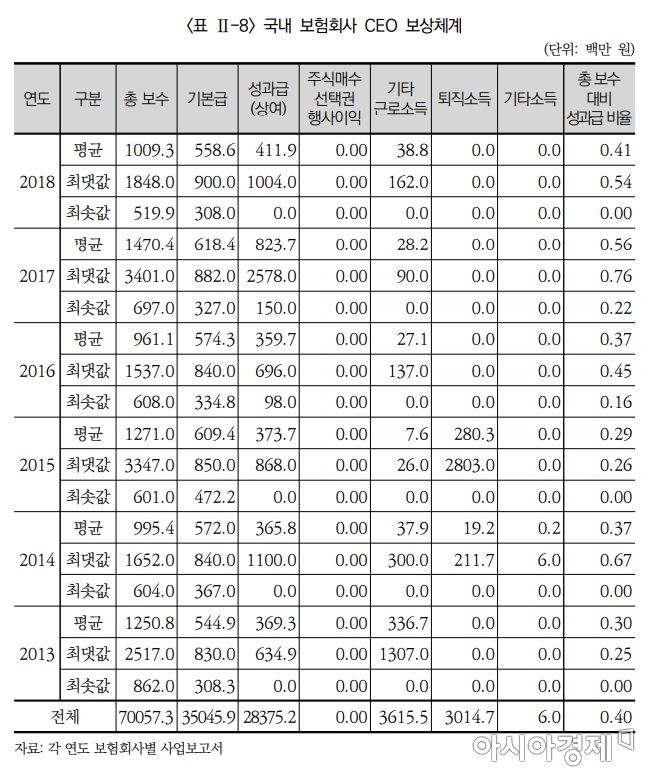
[Asia Economy Reporter Oh Hyung-gil] Thirty-four domestic insurance companies have paid a total of 70 billion KRW in compensation to their chief executive officers (CEOs) over the past six years. On average, each CEO received an annual salary of 1.14 billion KRW.
According to the report "Study on the Compensation System for Insurance Company Executives" by the Korea Insurance Research Institute on the 28th, from 2013 to 2018, the average annual salary of CEOs in domestic insurance companies was 1.15 billion KRW for life insurance and 1.13 billion KRW for non-life insurance, with the industry average being 1.14 billion KRW.
CEO salaries showed fluctuations each year due to significant changes in performance bonuses.
In 2013, the average CEO salary was 1.25 billion KRW, which decreased to 995 million KRW in 2014. It then increased to 1.271 billion KRW in 2015 but dropped again to 961 million KRW in 2016.
In 2017, it rose to 1.47 billion KRW before falling to 1.09 billion KRW in 2018. This variation is believed to be due to changes in base salary and performance bonuses depending on the insurance companies’ performance each year.
Notably, the difference between the highest and lowest CEO compensation each year was found to be three to five times, indicating a significant disparity in CEO pay among insurance companies.
In 2018, the CEO with the highest compensation received 1.848 billion KRW, while the lowest was only 519 million KRW.
Additionally, the average compensation for insurance company executives was found to be 327 million KRW.
The report pointed out that the ratio of performance bonuses to total CEO compensation was 40.5% (39.1% for life insurance, 41.8% for non-life insurance), indicating a relatively low proportion of performance-linked pay in total compensation.
For executives, the proportion of performance bonuses in total compensation was 34.6% for life insurance companies and 37.4% for non-life insurance companies.
The report emphasized, "In the compensation system for insurance company executives, the proportion of fixed pay such as base salary should be reduced, and the proportion of performance-based pay directly linked to the company’s medium- to long-term performance should be increased to ensure a close correlation between compensation and performance."
In South Korea, under the Capital Markets Act, companies are required to disclose individual compensation details and specific calculation criteria and methods for executives whose pay exceeds 500 million KRW through business reports.
The report evaluated, "Since companies are allowed to autonomously determine the criteria and methods for calculating compensation, the level of disclosure varies. Many insurance companies simply disclose the total amount of compensation without revealing the specific formulas or grounds for calculating the pay."
Meanwhile, the research team collected and organized compensation data for executives and CEOs from 34 insurance companies (23 life insurance and 11 non-life insurance) that disclosed executive compensation in business reports and annual compensation system reports from 2013, when disclosure of executive compensation for listed companies began, through 2018.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
!["The Woman Who Threw Herself into the Water Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag"...A Grotesque Success Story That Shakes the Korean Psyche [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















