 Yearly patent application status data for biometric authentication and decentralized ID technologies from 2015 to September 2020. Provided by the Korean Intellectual Property Office.
Yearly patent application status data for biometric authentication and decentralized ID technologies from 2015 to September 2020. Provided by the Korean Intellectual Property Office.
[Asia Economy (Daejeon) Reporter Jeong Il-woong] As next-generation authentication technologies that will replace public certificates attract attention, patent applications for related technologies are also increasing accordingly. Next-generation authentication technologies gaining attention include ‘biometric recognition technologies’ using fingerprints, irises, faces, veins, etc., and ‘decentralized ID technologies’ that use blockchain to distribute and store customer identification information.
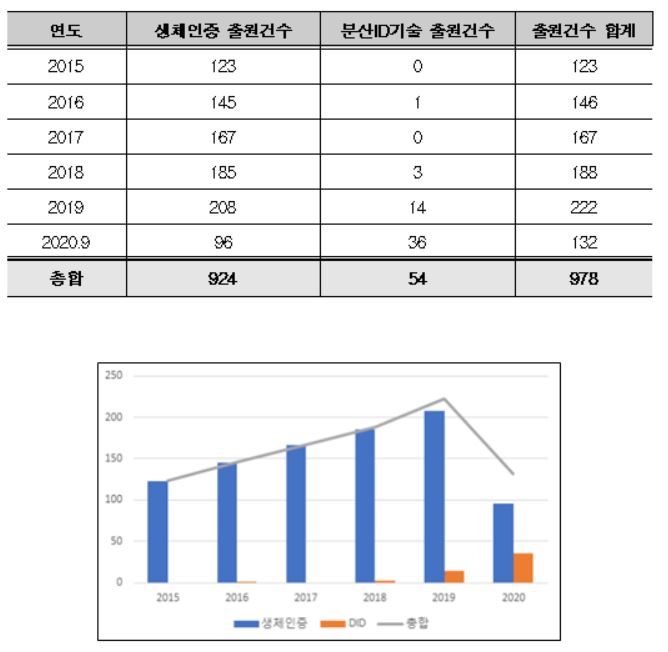
According to the Korean Intellectual Property Office on the 23rd, patent applications for next-generation authentication technologies increased from 123 cases in 2015 to 222 cases in 2019. This represents an average annual growth rate of 16% during this period.
The high interest in next-generation authentication technologies and the increase in patent applications were also influenced by the upcoming full revision of the ‘Electronic Signature Act’ scheduled to be enforced at the end of this year.
The Electronic Government Act was enacted in 2001, and since then, public certificates have been used as an essential authentication method for internet banking.
However, public certificates caused inconvenience to users due to the need to store them on separate storage devices and the requirement to install additional programs such as ActiveX. As a result, the government decided to amend the Electronic Government Act to remove the regulation that ‘only public certificates must be used.’
This became the background for the renewed attention to biometric recognition technologies and decentralized ID technologies, which are considered next-generation authentication technologies.
In fact, as discussions on the amendment of the Electronic Government Act progressed, patent applications related to these technologies noticeably increased. Biometric recognition technology patent applications rose from 123 cases in 2015 to 208 cases in 2019, an average annual increase of 14%, while decentralized ID technology patent applications increased from zero cases in 2015 to 36 cases by September 2020.
Among these, biometric recognition technology is considered highly secure because it uses some of the human body’s biometric information, which is difficult to replicate, and it appears to steadily increase patent applications in fields such as smartphones and financial payments.
Additionally, decentralized ID technology focuses on preventing forgery and tampering by encrypting personal identification information using personal data such as names, addresses, and resident registration numbers through blockchain technology. Recently, competition for leadership in this related market has become more apparent. In fact, big tech companies such as Microsoft and IBM are reportedly responding quickly in the decentralized ID technology field and developing related services.
Um Chan-wang, Director of the Telecommunications Technology Examination Bureau at the Korean Intellectual Property Office, emphasized, “Authentication technology is considered an essential requirement to activate non-face-to-face services in the post-COVID era,” adding, “In the future, authentication technologies such as public key infrastructure (PKI), biometric recognition, and decentralized ID technologies are expected to be interconnected and utilized together, making securing intellectual property rights important for market dominance.”
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
















