Fair Trade Commission Analyzes and Publishes '2019 Internal Transaction Status' Among Affiliates of Publicly Disclosed Business Groups
Proportion of Publicly Disclosed Business Groups at 12.2%, Similar to Previous Year
Internal Transaction Ratio of Top 10 Groups with Controlling Shareholders Shows Increasing Trend
Especially High Internal Transaction Ratio of 19.1% in Companies Where Second-Generation Controlling Shareholders Hold Over 20% Stake
[Sejong=Asia Economy Reporter Joo Sang-don] It has been found that unlisted companies have a higher proportion of internal transactions than listed companies, and business groups with controlling shareholders have a higher internal transaction ratio than those without. In particular, companies where the second-generation controlling shareholder holds more than 20% of shares showed a high internal transaction ratio.
The Korea Fair Trade Commission (KFTC) analyzed and disclosed on the 12th the status of '2019 goods and service transactions (internal transactions)' conducted among affiliates of publicly disclosed business groups in 2020.
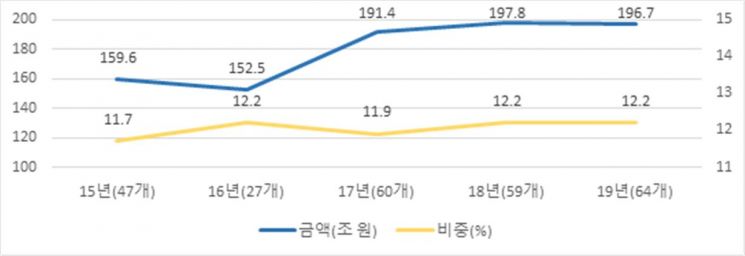
According to this, the total amount of internal transactions within publicly disclosed business groups this year was KRW 196.7 trillion, with a ratio of 12.2%, maintaining a similar level to last year (KRW 197.8 trillion, 12.2%). However, the internal transaction ratio of the top 10 groups with controlling shareholders increased by 0.3 percentage points from 13.8% to 14.1%.
The groups with the highest internal transaction ratios were Celltrion (37.3%), SK (26.0%), and Taeyoung (21.4%) in that order. The groups with the largest transaction amounts were SK (KRW 41.7 trillion), Hyundai Motor (KRW 37.3 trillion), and Samsung (KRW 25.9 trillion).
The internal transaction ratio was higher in unlisted companies (19.9%) than in listed companies (8.5%), and higher in groups with controlling shareholders (12.5%) than in those without (10.4%). Among the total 1,955 affiliates analyzed, 1,527 had internal transactions, and 668 companies had an internal transaction ratio exceeding 30%.
Over the past five years, the internal transaction ratio of publicly disclosed business groups has fluctuated around 12%, and the transaction amount has remained at a similar level since 2017, when the scope of large business groups expanded. The KFTC evaluated that this indicates the culture of preferential internal transactions has not spread even after the full enforcement of the prohibition on private interest infringement under the Fair Trade Act in 2015.
The internal transaction ratio and amount of the top 10 groups with controlling shareholders (based on 2020 designation) have shown an increasing trend over the past five years. The ratio rose from 13.1% in 2015 to 14.1% in 2019, and the amount increased from KRW 124.8 trillion to KRW 150.5 trillion during the same period.
A notable characteristic was confirmed in the relationship between the second-generation controlling shareholder's stake and the internal transaction ratio. Companies where the second-generation controlling shareholder holds 20% or more showed an internal transaction ratio of 19.1%, significantly higher than the 12.3% ratio of companies with less than 20% stake. The overall internal transaction ratio of all analyzed companies was 12.2%.
The internal transaction ratio of companies subject to private interest infringement regulations was 11.9%, with an amount of KRW 8.8 trillion, whereas companies in regulatory blind spots had a ratio of 11.7% and an amount of KRW 26.5 trillion.
Although the internal transaction ratios between regulated companies and those in blind spots were similar, considering the number of companies (176 and 343 respectively) and transaction amounts (KRW 8.8 trillion and KRW 26.5 trillion), the average internal transaction amount per company was about 1.5 times higher in companies in the blind spot.
The internal transaction ratio of listed companies with a controlling family stake between 29% and less than 30%, i.e., companies on the borderline of private interest infringement regulation, reached 23.1%. Hyundai Glovis (Hyundai Motor), LG (LG), KCC Construction & Korea Auto Glass (KCC), and Taeyoung Construction fall into this category.
Both companies subject to private interest infringement regulations and those in blind spots had very high proportions of private contracts, at 95.4% and 95.3% respectively. Compared to the previous year, these proportions increased by 5.5 and 4.9 percentage points respectively.
A KFTC official stated, "Given concerns about intensifying general concentration, we will continue and strengthen monitoring and corrective activities against unfair internal transactions," adding, "The amendment to the Fair Trade Act currently submitted to the National Assembly should be promptly passed to enable monitoring of private interest infringement activities in regulatory blind spots."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.