Clarification of Thermal Decomposition Mechanism of Electrode Materials
Aluminum Element Deficiency During Charging Reduces Thermal Stability
Foundation for Designing Safe Materials for 3rd Generation Electric Vehicles
 An illustrative diagram depicting the role of aluminum in reducing the risk of battery fires in NCA (Nickel, Cobalt, Aluminum), a widely used cathode material for electric vehicles.
An illustrative diagram depicting the role of aluminum in reducing the risk of battery fires in NCA (Nickel, Cobalt, Aluminum), a widely used cathode material for electric vehicles.
[Asia Economy Reporter Junho Hwang] Amid recent consecutive battery fire incidents in electric vehicles, a research team has revealed the causes of battery fires. The researchers suggested that the thermal instability caused by the chemical composition of cathode materials could be the cause of fires, and controlling this could prevent such incidents.
Dr. Wonyoung Jang from the Energy Storage Research Group and Dr. Seungmin Kim from the Carbon Convergence Materials Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced on the 3rd that their joint research team developed a real-time analytical platform (analysis method) to evaluate the thermal stability of battery cathode materials. The related research findings are scheduled to be published in the latest issue of the international journal Nano Energy.
Fire Causes Arise Depending on Cathode Material Composition
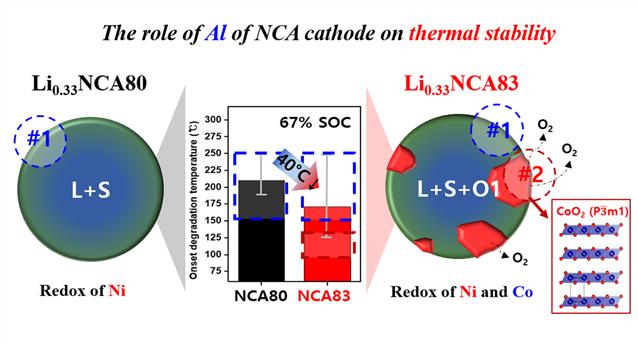 Investigation of the Cause of Thermal Stability Differences According to the Chemical Composition of NCA Cathode Material in Actual Fully Charged State
Investigation of the Cause of Thermal Stability Differences According to the Chemical Composition of NCA Cathode Material in Actual Fully Charged State
The research team elucidated changes in the thermal decomposition mechanism according to subtle chemical composition variations in high-nickel cathode materials for electric vehicles. Using transmission electron microscopy analysis techniques such as electron energy spectroscopy and electron diffraction analysis, the team closely examined changes in the crystal structure of the electrode and chemical composition as temperature increased. As a result, they identified the causes of reduced thermal stability in batteries due to chemical composition in NCA (Nickel-Cobalt-Aluminum) cathode materials and clarified the role of constituent elements in ensuring battery safety.
The team reported that increasing the nickel content in NCA cathode materials increases battery capacity but significantly reduces thermal stability at actual upper charge states (67% reaction of total lithium ions). Further analysis revealed that a deficiency of aluminum, which does not participate in the redox reaction, leads to the formation of a new phase (O1 Phase) during charging that can reduce thermal stability. The unstable surface structure of this new phase was identified as the cause of the decreased thermal stability.
Battery fires are mainly known to occur due to intense exothermic reactions between charged oxide-based cathode materials and flammable liquid electrolytes, and this study specifically clarified this mechanism.
Development of High-Performance Cathode Materials Possible by Doping Trace Elements
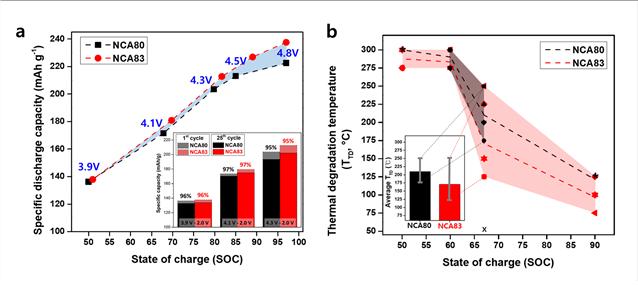 Trade-off Relationship Between Battery Performance and Thermal Stability Due to Nickel and Aluminum Substitution in NCA Cathode Materials
Trade-off Relationship Between Battery Performance and Thermal Stability Due to Nickel and Aluminum Substitution in NCA Cathode Materials
Dr. Wonyoung Jang stated, "Recently, electric vehicle fires have occurred worldwide, with batteries often being the cause. This study confirmed the importance of chemical composition design to secure thermal stability in the development of high-performance cathode materials."
Dr. Seungmin Kim added, "Securing the thermal stability of the cathode material itself, which is the starting point of the exothermic reaction, plays a very important role in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Through the advanced analytical platform developed this time, it will be possible to understand the effects of doping trace elements and develop high-performance cathode materials with ensured stability in the future."
Meanwhile, the cathode of a battery plays a key role in determining charging capacity (driving range). Cathode materials are manufactured by blending various components such as nickel, cobalt, aluminum, or nickel, manganese, cobalt in appropriate ratios. The third-generation cathode materials currently under development for electric vehicles have nickel content exceeding 80%, making it essential to improve the resulting stability degradation.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
















