'Bone Fixation Implant' Developed Inspired by Beolrejabitongpul
Slippery Lubricant Prevents Surface Bacterial Adhesion
Expected to Contribute to Infection and Inflammation Prevention
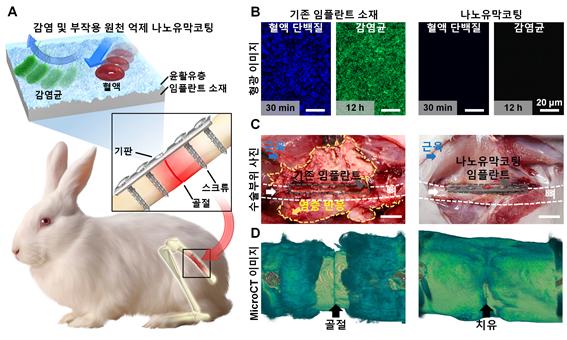
[Asia Economy Reporter Junho Hwang] The pitcher plant repels contaminants such as water or dust using the nanostructures on its surface and slippery lubricant, attracting only insects into its trap. Utilizing these characteristics, an orthopedic implant for bone fixation that prevents infection or inflammation has been developed.
The National Research Foundation of Korea announced that Professor Jung Jeongmok of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at Yonsei University, Professor Jang Wooyoung of Orthopedics at Korea University, and others jointly developed a surface coating technology that reduces concerns about infection or immune rejection reactions in orthopedic implant materials. The related research paper was published on the 29th (Korean time) in the international academic journal 'Science Advances.'
Preventing Infection After Bone Fixation Implant Surgery Using Nanotechnology
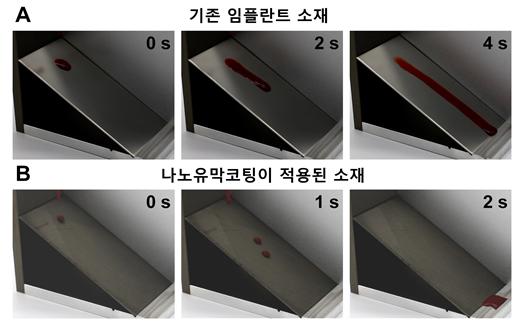
The research team developed a durable nano-lubricant coating technology for orthopedic implant surfaces that can prevent the adhesion of bacteria, viruses, and immune proteins that cause inflammation. The surface coated with this technology has lubricant components uniformly applied to the surface nanostructures, preventing the adsorption of blood containing infectious bacteria or immune rejection factors.
In particular, this coated surface has self-healing properties against mechanical damage that may occur during surgery. Additionally, the coating function was shown to be maintained for several weeks in vivo in animal models.
When the research team examined the implant insertion site in an actual fracture rabbit model, they confirmed that no infection or inflammation occurred on implants with the nano-lubricant coating applied. Furthermore, bone regeneration at the fractured site was effectively achieved, comparable to the uninfected control group.
Potential Applications in Urology Catheters and More
The research team expects that the proposed coating technology can also be applied to polymer materials besides metals and plans to conduct follow-up studies on its applicability to urology catheters, stents, and implantable medical electronic devices.
Meanwhile, metal implants used in fracture treatment or artificial joint insertion mainly use antibiotic coatings on their surfaces to prevent infection or inflammation. However, concerns remain about side effects such as infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria, inflammation, nerve damage, drug side effects, and hypersensitivity reactions to antibiotics themselves. Accordingly, hydrogel-based surface coatings have been attempted, but orthopedic implant materials are exposed to strong mechanical stimuli during surgery, and due to the nature of orthopedic surgeries requiring treatment for several weeks or more, there are technical difficulties in maintaining long-term coating performance.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.