From 2G Phone Dominance to Decline, Then Revival as a 5G Leader
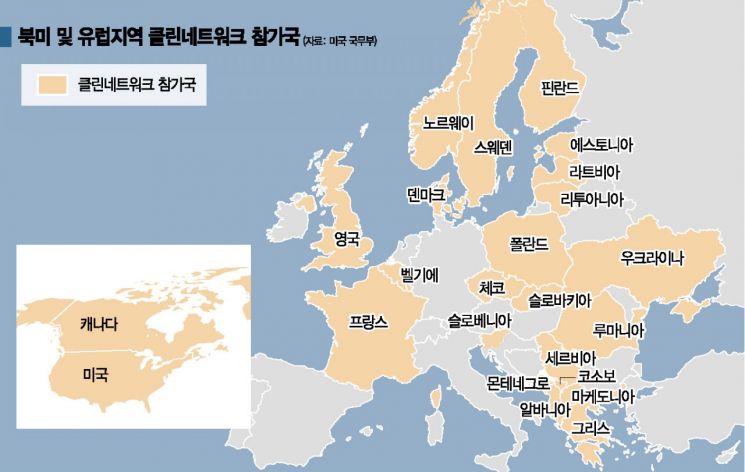
Emerges as the Biggest Beneficiary of the US-Led Anti-China Clean Network
Secures Consecutive Contracts Including NASA Moon Base Communications and NATO Headquarters Belgium 5G Supply Network
[Asia Economy Reporter Hyunwoo Lee] Nokia of Finland, which once dominated the global mobile phone market, is emerging as the biggest beneficiary of the U.S. crackdown on Chinese advanced technology companies. As the U.S. demands countries worldwide to exclude Chinese companies like Huawei from 5G network projects in the so-called 'Clean Network' initiative, Nokia has begun to attract attention as a countermeasure. Nokia has simultaneously secured 5G network projects from NASA and NATO and has signed 100 contracts for 5G equipment supply worldwide to date.
According to UK IT specialist media Telecoms.com on the 26th (local time), Verizon and AT&T, considered the largest U.S. mobile carriers, recently selected Nokia as their partner for private enterprise 5G network cooperation projects. Earlier, on the 9th, Nokia was chosen as the 5G network supplier for NATO and the European Union (EU) headquarters in Belgium, and on the 19th, it was named the 4G and 5G network supplier for NASA's manned lunar base.
The recent series of orders can be called Nokia's revival. Nokia was the absolute leader in 2G phones until the 2000s. In 2008, its global market share was 39.8%, meaning 4 out of every 10 mobile phones sold were Nokia products. However, as smartphones like the iPhone became dominant, Nokia declined and eventually sold its mobile phone business to Microsoft (MS) in 2013. While it achieved its highest revenue of 50.7 billion euros (about 67.7 trillion KRW) in 2008, it plummeted to 11.8 billion euros in 2014 within six years. Since then, it has gradually recovered, recording 23.3 billion euros in revenue last year.
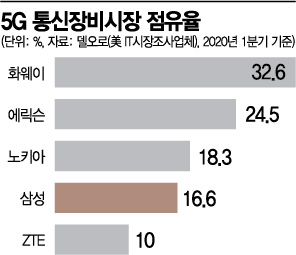
Nokia shifted its focus from mobile phones to telecommunications equipment. However, until the first quarter of this year, the 5G telecommunications equipment market was dominated by China's Huawei. Huawei's market share was 32.6%, ranking first, followed by Sweden's Ericsson at 24.5%. Nokia was third with 18.3%, followed by South Korea's Samsung Electronics (16.6%) and China's ZTE (10.0%) in fourth and fifth places, respectively.
The turning point came when the U.S. government began actively excluding Chinese companies from 5G network projects for national security reasons through the Clean Network initiative. As the expulsion of Chinese companies began mainly in Europe, orders started pouring in for Nokia and Ericsson. As of the 7th, Nokia had signed 100 contracts for 5G equipment, second only to Ericsson's 112 contracts.
However, Nokia is expected to surpass Ericsson in the future. Becoming the 5G network supplier for NASA and NATO is a clear example. This sector is intertwined with national defense and is a sensitive area for the U.S. government, which indicates a high level of trust in Nokia.
Interest in Nokia has increased further in the U.S. since February, when the U.S. Department of Justice suggested acquiring stakes in Nokia and Ericsson to curb Huawei's dominance. According to The New York Times (NYT), in February, U.S. Attorney General William Barr stated at a conference hosted by the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) that "to counter Huawei's dominance in 5G networks, the U.S. should directly acquire controlling stakes in Nokia and Ericsson or form consortia with allies," drawing attention. Particularly, Nokia is considered easier to acquire stakes in than Ericsson because U.S. private equity funds hold a high percentage of Nokia's shares.
According to Forbes, Nokia's largest shareholder is the Finnish state-owned investment company Solidium, owning about 5.1%. However, more than 60% of the total shares are reportedly held by U.S.-based private equity funds. Forbes also forecasts the possibility of mergers and acquisitions (M&A) by U.S. companies such as Qualcomm, which has cooperated with Nokia for over 14 years.
On the other hand, Ericsson has a high shareholding rate by Swedish capital, making it difficult for the U.S. to control. Ericsson's shares are largely owned by Swedish capital, with the Swedish venture capital group Cevian Capital holding 9%. In June, B?rje Ekholm, CEO of Ericsson, also drew a line in an interview with Bloomberg, stating, "I oppose U.S. government control over management" and "I do not want to get involved in the U.S.-China trade dispute."
Of course, where there is light, there is shadow. While Nokia is gaining attention in Western countries centered on the U.S., it is completely excluded in China. Nokia is perceived as the leading company of the U.S. Clean Network. Ericsson is barely maintaining its business in China. According to CNBC, Ericsson holds about a 10% market share in China's 5G telecommunications business. In March and April, Ericsson was the only foreign company to receive 11% of the total 5G telecommunications equipment orders from Chinese telecom operators China Mobile and China Telecom.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![User Who Sold Erroneously Deposited Bitcoins to Repay Debt and Fund Entertainment... What Did the Supreme Court Decide in 2021? [Legal Issue Check]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026020910431234020_1770601391.png)














