[Asia Economy Reporter Junho Hwang] Domestic researchers have compiled an encyclopedic summary covering the structure, characteristics, aggregation, and interactions of tau protein?considered a major cause of degenerative brain diseases such as dementia?drawing significant attention from the academic community.
The research team led by Professor Youngho Lee of the Bio Convergence Research Division at the Korea Basic Science Institute and Professor Mihi Lim of the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology announced on the 12th that their findings were published in the international journal Chem.
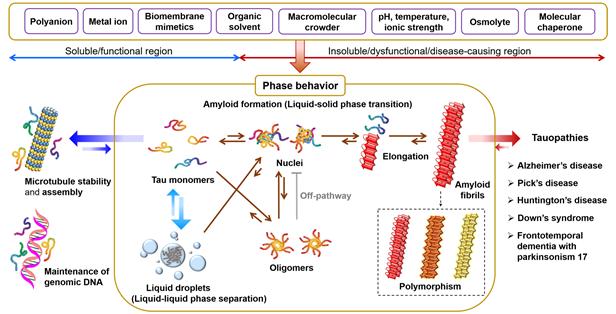
The team organized research results from scientists worldwide regarding the structure and properties of tau protein. They also systematized the environmental factors that influence tau protein when it functions properly and when it becomes a cause of disease. Professor Lee devised a 'phase diagram' that visually represents the interactions and aggregation states of tau protein for easier understanding.
Professor Lee said, "I hope this paper serves as an encyclopedia on tau protein, greatly aiding students and experts alike," adding, "A deep understanding of tau protein interactions could lead to new ideas for treating Alzheimer's disease."
Meanwhile, 'tau tangles,' formed by the aggregation of tau protein, are gaining attention as a cause of degenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. Tau protein, which exists dissolved in a liquid state inside nerve cells, attaches to the intracellular skeleton (microtubules) to stabilize nerve cell structure and assist cell differentiation. However, when tau protein detaches from the intracellular skeleton, environmental factors cause protein aggregation, transforming it from a liquid to a solid state, forming tau tangles that kill nerve cells.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.