 Due to the influence of yellow dust, the cityscape viewed from Inwangsan Mountain in Seoul appeared hazy on the 12th, when fine dust levels were forecasted to be poor. The Korea Meteorological Administration stated, "Fine dust is expected to be at a 'poor' level in the metropolitan area and 'moderate' in other regions." They added, "However, in the afternoon, the metropolitan area is expected to temporarily reach a 'very poor' level, and other regions are expected to temporarily reach a 'poor' level." Photo by Kim Hyun-min kimhyun81@
Due to the influence of yellow dust, the cityscape viewed from Inwangsan Mountain in Seoul appeared hazy on the 12th, when fine dust levels were forecasted to be poor. The Korea Meteorological Administration stated, "Fine dust is expected to be at a 'poor' level in the metropolitan area and 'moderate' in other regions." They added, "However, in the afternoon, the metropolitan area is expected to temporarily reach a 'very poor' level, and other regions are expected to temporarily reach a 'poor' level." Photo by Kim Hyun-min kimhyun81@
[Asia Economy Reporter Junho Hwang] Global warming has been identified as the cause of high concentrations of fine dust in South Korea. Due to global warming, there has been a continuous decrease in surface wind speeds and stabilization of the atmosphere in Northeast Asia, including South Korea, which has caused fine dust to become trapped over the Korean Peninsula.
A research team led by Professor Jinho Yoon of the Department of Earth and Environmental Engineering at Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology analyzed long-term observational data spanning 60 years since 1958 and multiple global climate models called the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 5 (CMIP5). They recently published these findings in the international journal Atmospheric Environment on the 5th.
First, the research team identified that over the past 50 years, as global warming progressed, the temperature in the lower atmosphere increased faster than at the surface, leading to a steady stabilization of the atmosphere. They also analyzed that this trend has recently intensified. According to the team, this causes fine dust transported over long distances from China and fine dust generated domestically to become trapped over the Korean Peninsula, thereby exacerbating fine dust levels.
In particular, the increase in atmospheric stability was observed across Northeast Asia, including the Korean Peninsula, China, and Japan. The impact of global warming on atmospheric stability varies slightly by region but still shows an increasing trend.
Professor Jinho Yoon stated, "The research results suggest that the increase in atmospheric stability may raise the likelihood of high concentrations of fine dust. Especially on the Korean Peninsula, despite the government's continuous efforts to reduce air pollution, cases of high fine dust concentrations are still reported, and the long-term stagnation of the atmosphere under these conditions is a significant problem."
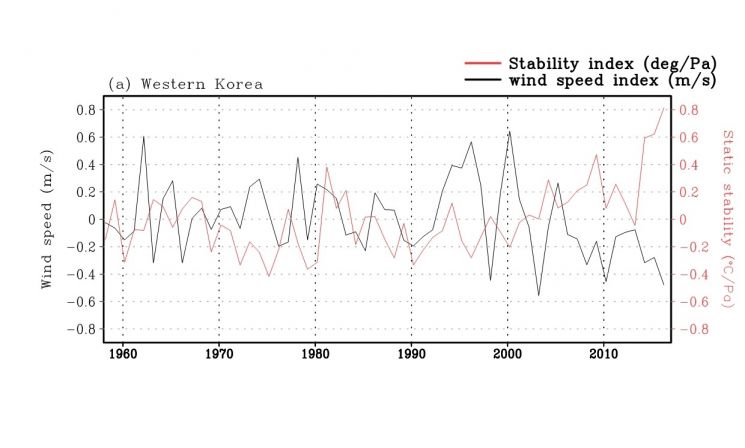 This shows the time series trend of surface wind speed (black line) and static stability (red line) in the western region of the Korean Peninsula from 1958 to 2016. It can be observed that static stability increases and wind speed decreases from February to May in the western region of the Korean Peninsula, indicating atmospheric stabilization. This suggests that prolonged atmospheric stabilization from late winter to spring may contribute to the deterioration of air quality.
This shows the time series trend of surface wind speed (black line) and static stability (red line) in the western region of the Korean Peninsula from 1958 to 2016. It can be observed that static stability increases and wind speed decreases from February to May in the western region of the Korean Peninsula, indicating atmospheric stabilization. This suggests that prolonged atmospheric stabilization from late winter to spring may contribute to the deterioration of air quality.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![From Hostess to Organ Seller to High Society... The Grotesque Scam of a "Human Counterfeit" Shaking the Korean Psyche [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















