2020 Large Business Group Share Ownership Status
Blind Spots in Regulation of Private Interest Appropriation by the Controlling Family Increase
Possibility of Indirect Affiliate Investment via Public Interest Corporations and Overseas Affiliates Rises
Private Equity Fund IMM Investment Has Lowest Controlling Family Shareholding at 0.2%
Top 10 Groups' Affiliate Shareholding Increased from 43% to 54.2% Over 20 Years
Blind Spot Companies Increase in Hyosung, Hoban Construction, GS, Taeyoung, Netmarble, Shinsegae, Harim
KG Newly Designated as Publicly Disclosed Business Group... 10 Additional Circular Shareholding Chains
Financial and Insurance Companies' Investment in Non-Financial Affiliates Rose from 41 to 53 Last Year
Public Interest Corporation Investments Increased from 124 to 128, Overseas Affiliates from 47 to 51
 Former Chairman Park Sam-gu of Kumho Asiana Group. On the 27th, the Fair Trade Commission judged that Park's act of systematically supporting Kumho Express, which is at the top of the group's governance structure centered on the owner, by using the in-flight meal business to strengthen his control within the group, violated the Fair Trade Act and reported him to the prosecution. Photo by Kim Hyun-min kimhyun81@
Former Chairman Park Sam-gu of Kumho Asiana Group. On the 27th, the Fair Trade Commission judged that Park's act of systematically supporting Kumho Express, which is at the top of the group's governance structure centered on the owner, by using the in-flight meal business to strengthen his control within the group, violated the Fair Trade Act and reported him to the prosecution. Photo by Kim Hyun-min kimhyun81@
[Asia Economy Reporter Moon Chaeseok] It has been revealed that controlling families still dominate entire groups through affiliate investments with only 3.6% shareholding.
The blind spots in regulation of private interest appropriation by controlling families are widening, and the possibility of indirect affiliate investments through public interest corporations, overseas affiliates, and financial and insurance companies has increased.
Controlling Family Shareholding at 3.6%... IMM Investment Lowest at 0.2%
The Korea Fair Trade Commission (KFTC) announced on the 31st the '2020 Publicly Disclosed Business Group Share Ownership Status' containing these details.
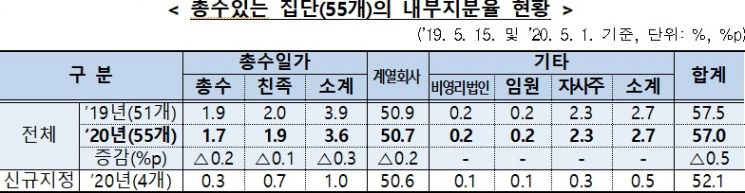
According to the KFTC, among the 64 publicly disclosed business groups designated this year, the internal shareholding ratio of 55 groups with controlling families was 57.6%, down 1 percentage point from last year.
The controlling family shareholding was only 3.6% (1.7% controlling family members, 1.9% relatives). Affiliates held 50.7%, and others (executives, non-profit corporations, treasury stocks) accounted for 2.7%.
Business groups with low controlling family shareholding include IMM Investment (0.2%), SK and Hyundai Heavy Industries (each 0.5%), Kumho Asiana (0.6%), and Harim (0.8%) in that order.
Affiliate Shareholding Steadily Increased Over 20 Years... Concerns Over Indirect Investments
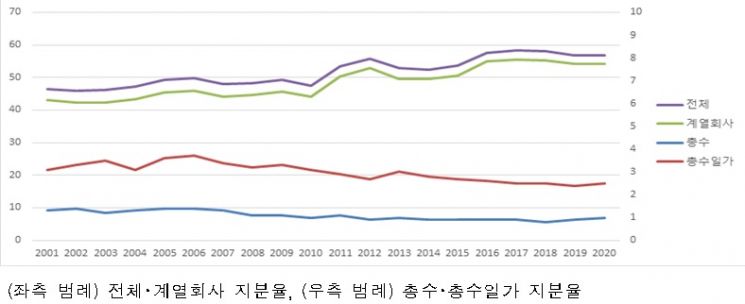
Over the past 20 years, while controlling family shareholding declined, affiliate shareholding increased.
Looking at the internal shareholding trends of the top 10 groups from 2001 to 2020, controlling family shareholding fell from 1.3% to 1%, but affiliate shareholding rose from 43% to 54.2%.
Among 50 groups with controlling families, 210 companies are subject to private interest appropriation regulations, down 9 from last year, but the number of blind spot companies increased by 12 to 388.
The KFTC defines 'blind spot companies' as ▲listed companies with controlling family shareholding between 20% and less than 30% (listed blind spot companies), ▲subsidiaries holding more than 50% shares in companies subject to private interest appropriation regulations, and ▲subsidiaries holding more than 50% shares in listed blind spot companies.
The average controlling family shareholding in companies subject to private interest appropriation regulations was 56.6%, up 4.6 percentage points from 52% last year.
Among 30 listed blind spot companies, five companies with controlling family shareholding between 29% and less than 30% are Hyundai Glovis, LG, KCC Construction, Korea Auto Glass, and Taeyoung Construction.
The groups with the most blind spot companies are Hyosung (32), Hoban Construction (19), GS, Taeyoung, Netmarble (each 18), Shinsegae, and Harim (each 17).
Monitoring Investments by Financial and Insurance Companies, Public Interest Corporations, and Overseas Affiliates
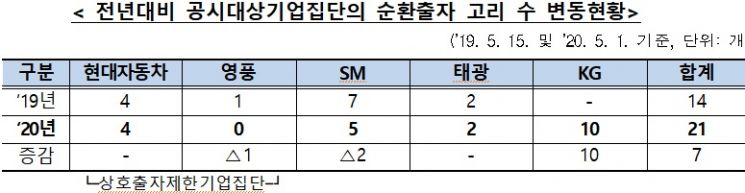
As of May 1, among publicly disclosed business groups, Hyundai Motor Company (Hyundai Motor), Taekwang, SM, and KG hold 21 circular shareholding chains, an increase of 7 from 14 last year.
Youngpoong completely eliminated its existing circular shareholding. SM reduced its circular shareholding chains from 7 last year to 5. KG was newly designated as a publicly disclosed business group this year, adding 10 existing circular shareholding chains.
The number of non-financial affiliates invested in by financial and insurance companies increased to 53, up 12 from 41 last year. The number of affiliates invested in by public interest corporations rose to 128, up 4 from last year, and the number of domestic affiliates invested in by overseas affiliates increased by 4 to 51.
The amendment to the Fair Trade Act approved at the Cabinet meeting on the 25th includes restrictions on voting rights and disclosure obligations (public interest corporations), exclusion from exceptions for mergers unrelated to hostile M&A (financial and insurance companies), and disclosure obligations (overseas affiliates).
Sung Kyung-je, Director of the Corporate Group Policy Division at the KFTC, pointed out, "It is a reality that acts contrary to the fundamental purpose of institutions are occurring, such as financial and insurance companies increasing non-financial affiliates using customer assets rather than their own capital, and using public interest corporations to park affiliate shares under the pretext of social contribution while special related parties exercise voting rights on the board."
Director Sung emphasized, "The blind spots in regulation of private interest appropriation by controlling families are expanding, and cases where controlling power may be indirectly expanded through public interest corporations or overseas affiliates are increasing, so institutional improvements are urgently needed."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.