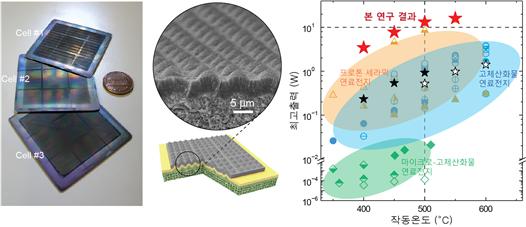
 A photo of a three-dimensional multiscale solid oxide fuel cell fabricated on a large area (left) and a graph documenting that the results of this study demonstrate the world's highest performance for low-temperature ceramic fuel cells.
A photo of a three-dimensional multiscale solid oxide fuel cell fabricated on a large area (left) and a graph documenting that the results of this study demonstrate the world's highest performance for low-temperature ceramic fuel cells.
[Asia Economy Reporter Junho Hwang] Domestic researchers have developed a high-performance solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC). This cell addresses various drawbacks of solid oxide fuel cells, such as high operating temperatures and performance degradation. It is being evaluated as a cornerstone for the commercialization of next-generation solid oxide fuel cells that can be used from power generation fuel cells to batteries for smartphones.
Dr. Hyungcheol Kim's research team at the Energy Materials Research Group of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), in collaboration with Professor Mansoo Choi's team at Seoul National University, announced on the 14th that they have developed a high-performance solid oxide fuel cell with a three-dimensional structure. The research results were published in the international journal Energy & Environmental Science.
Development of Low-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell
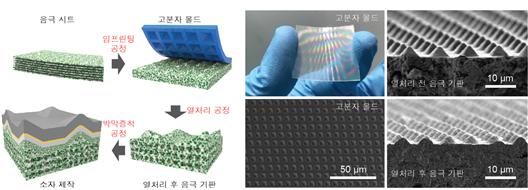 The research team fabricated three-dimensional multiscale solid oxide fuel cells by combining a thin-film deposition process with a ceramic micropatterning process, which involves imprinting a polymer mold onto the anode tape followed by heat treatment.
The research team fabricated three-dimensional multiscale solid oxide fuel cells by combining a thin-film deposition process with a ceramic micropatterning process, which involves imprinting a polymer mold onto the anode tape followed by heat treatment.
The research team significantly increased the commercialization potential of solid oxide fuel cells through this study. They resolved most of the drawbacks of solid oxide fuel cells by using ceramic micropatterning and thin-film-based three-dimensional processing technologies. Solid oxide fuel cells are devices that use solid oxides as electrolytes to convert chemical energy into electrical energy.
The team developed a ceramic micropatterning process to create a three-dimensional anode substrate by engraving micrometer-sized pyramid shapes on a polymer-ceramic composite anode substrate. Then, by stacking multiple layers through thin-film processes, they fabricated a multi-scale solid oxide fuel cell with a three-dimensional structure.
This cell has a three-dimensional structure with a large interfacial area, which enhances ion transport performance and reduces electrode reaction resistance. The research team reported that it showed more than 50% higher performance compared to conventional planar solid oxide fuel cells.
World-Class Performance
The research team demonstrated this cell with a large area of over 16㎠. The results showed an output of more than 13 watts at 500℃, which is the highest performance among existing low-temperature ceramic fuel cells worldwide. Notably, this cell did not show performance degradation even after long-term operation exceeding 500 hours.
Lowering the operating temperature to 600℃ or below is also a remarkable achievement. Conventional solid oxide fuel cells operate only at high temperatures above 750℃, making commercialization difficult due to issues such as reliability and processing costs.
Dr. Hyungcheol Kim of KIST stated, "There have been attempts to create micro three-dimensional structures in low-temperature solid oxide fuel cells, but this is the first study to simultaneously satisfy all evaluation criteria (performance, stability, large-area fabrication, and mass production)." He added, "The three-dimensional structured solid oxide fuel cell fabricated using ceramic micropatterning and thin-film processing technology is an innovative result that overcomes the technical limitations for the commercialization of next-generation ceramic fuel cells."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)















