 Professor Yoojongsung (right), Department of Energy Engineering, DGIST, and Hayoung Lee, Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program
Professor Yoojongsung (right), Department of Energy Engineering, DGIST, and Hayoung Lee, Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program
[Asia Economy Reporter Junho Hwang] A domestic research team has developed a new catalyst to replace the platinum catalyst, which accounts for 40% of the cost of hydrogen fuel cells. This catalyst, which uses magnesium, not only performs 2.7 times better than existing catalysts but is also more stable, and is expected to contribute to the development of more efficient hydrogen fuel cells.
The research team led by Professor Jongsung Yoo from the Department of Energy Engineering at Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology announced on the 24th that they introduced their research results on a new concept electrode catalyst that is more stable than the existing platinum catalyst for hydrogen fuel cells in the international academic journal ACS Energy Letters.
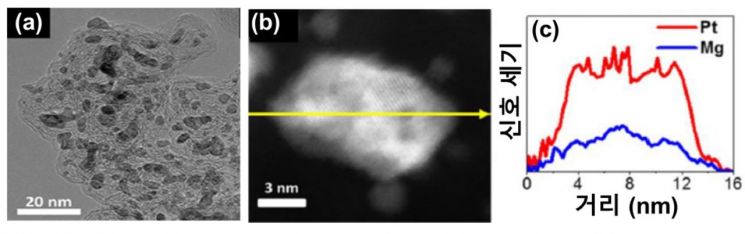
The research team focused on magnesium as a material to replace the platinum catalyst. They anticipated that a catalyst with high stability could be developed due to magnesium’s low melting point and electronic structural characteristics. To prevent the easy oxidation of magnesium, which is a material drawback, they devised a synthesis method using magnesium as a precursor. This method involves mixing carbon supports impregnated with platinum salt and magnesium metal powder, followed by high-temperature heat treatment at 650 degrees Celsius in a hydrogen-argon mixed gas atmosphere. Through this synthesis method, the team developed a platinum-magnesium alloy catalyst as magnesium melted and mixed with the platinum salt.
The research team reported that the mass activity, which indicates the catalytic performance of this catalyst, was 0.43 A/mg, showing about 2.7 times improved performance compared to the existing platinum catalyst’s activity of 0.16 A/mg. They also conducted fuel cell stability evaluations based on the U.S. Department of Energy standards and received an assessment that it is 1.5 times more stable than the existing platinum catalyst.
Professor Jongsung Yoo stated, "This research is a valuable achievement that reduces the expensive platinum content while improving activity and stability. The synthesis method of the catalyst is also simple, which can contribute to the mass production of hydrogen fuel cells. Through follow-up research, we will take the lead in creating a stable and eco-friendly energy production environment."
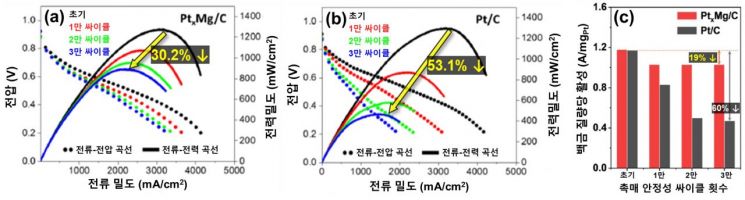 Graph of Fuel Cell Stability Evaluation Analysis of Platinum-Magnesium Catalyst and Commercial Platinum Catalyst
Graph of Fuel Cell Stability Evaluation Analysis of Platinum-Magnesium Catalyst and Commercial Platinum Catalyst
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.
![Clutching a Stolen Dior Bag, Saying "I Hate Being Poor but Real"... The Grotesque Con of a "Human Knockoff" [Slate]](https://cwcontent.asiae.co.kr/asiaresize/183/2026021902243444107_1771435474.jpg)










