[Asia Economy Reporter Junho Hwang] Domestic researchers have developed a technology that combines artificial intelligence and sensor technology to accurately measure the movement of surrounding joints with just one sensor. The research team expects this to become a new input system for wearable virtual and augmented reality devices.
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) announced on the 20th that a research team led by Professor Seongho Cho from the Department of Computer Science, in collaboration with Professor Seunghwan Ko from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Seoul National University, developed a flexible "skin-type sensor" that can accurately measure human body movements with minimal data by combining deep learning technology with sensors.
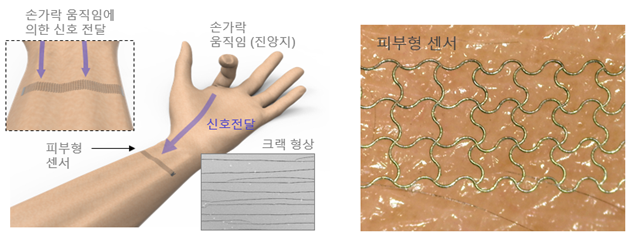
The skin-type sensor developed by the research team can precisely measure complex signals generated by human body movements using a minimal number of sensors attached to the skin.
It is possible to measure movements without motion capture cameras, and when using wearable devices, it can measure changes in the user's condition without location restrictions.
This sensor is a highly sensitive sensor based on "cracks." Cracks refer to fractures that occur in nanoparticles. The sensor changes the sensor values generated by the cracks to measure even subtle changes in wrist movements. The research team analyzed the sensor signals through a deep learning model, enabling the measurement of movements of various finger joints with a single sensor attached to the wrist.
Professor Seongho Cho of KAIST said, "This research is meaningful in that it presents a method to more effectively acquire real-time human information in actual environments by utilizing deep learning technology," and added, "Applying this measurement method will accelerate the era of widespread wearable augmented reality technology."
Professor Seunghwan Ko of Seoul National University also emphasized, "The effective combination of highly sensitive skin-type sensors and deep learning technology is expected to be utilized as a new input system for wearable virtual/augmented reality devices that will attract attention in the future."
Meanwhile, the results of this research were published in Nature Communications.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.