Potential Applications in Public Institutions, Finance, and 6G Communications
LG Uplus has established a key security technology as a domestic standard in preparation for the era of quantum computers, aiming to secure leadership in next-generation network security.
On December 30, LG Uplus announced that the Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) supported SDN interface and the NTRU lattice-based 'SOLMAE' digital signature method, which the company proposed to the Telecommunications Technology Association (TTA) of Korea, have been officially adopted as standards.
This standardization reflects LG Uplus’s strategy to proactively strengthen the security infrastructure across the nation and industries against the potential vulnerability of existing encryption systems following the advent of quantum computers, and to secure technological leadership in the global standards competition.
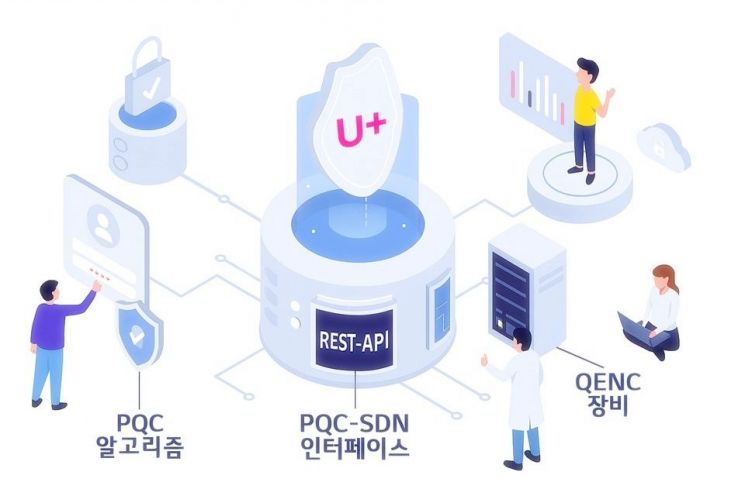
The first standard is an interface that enables interworking between encryption equipment supporting post-quantum cryptography (QENC) and software-defined networks (SDN). This technology was developed as part of the quantum testbed project led by the Korea Intelligence Information Society Agency, and it is significant as the first domestic standard to connect PQC equipment with SDN.
Through REST-API-based integration, it enables real-time status monitoring, certificate management, and policy configuration, and, as a widely compatible web standard, can easily connect with various systems. This technology is expected to greatly enhance security in ultra-high-speed network environments such as 5G and 6G mobile networks, data centers, and national backbone networks. LG Uplus has also filed a patent for this standard technology to further strengthen its technological competitiveness.
The second standard, the SOLMAE digital signature method, meets the security criteria of the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). It provides message integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation, fundamentally preventing forgery and tampering even in a quantum computing environment. In particular, by minimizing signature size and improving computational efficiency, it can be applied in resource-constrained environments such as IoT and embedded devices.
The SOLMAE standard was co-established with Kim Kwangjo, President of the International Cyber Security Research Institute (Honorary Professor at KAIST), and is expected to serve as a technological milestone leading future global discussions on PQC algorithm standards.
Based on these new standards, LG Uplus plans to launch pilot projects targeting public institutions and the financial sector starting next year, and to expand applications to various industries such as 6G mobile communications, autonomous vehicles, and smart factories.
Kim Jongcheol, Head of Wired Technology at LG Uplus, stated, "This standard will serve as the foundation for national core infrastructure security in the quantum computing era," and added, "We will lead the application of PQC across networks and digital signatures to secure an advantage in the global standards competition."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.