World's First Commercialization with No.1 Speed and Availability
Speed Doubled Since 2019
Quality-Related Consumer Complaints a Common Challenge Across Major Countries
[Asia Economy Reporter Cha Min-young] South Korea marks the 3rd anniversary of 5G commercialization on the 3rd. Since becoming the world's first country to commercialize 5G services in 2019, surpassing the United States, South Korea has consistently held the top position in terms of speed and availability over the past three years.
South Korea Ranks First in Mobile Network Experience
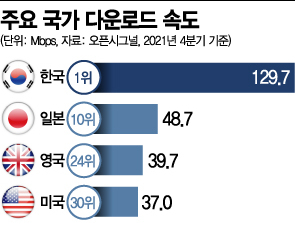
In the latest report titled "The Impact of 5G on Global Mobile Network Experience" by global research firm Opensignal on the 1st, South Korea ranked first in overall mobile network experience. As of the end of 2021, South Korea's average download speed was recorded at 129.7 Mbps. Compared to the time of 5G commercialization in 2019, the overall speed has more than doubled. Ian Fogg, Vice President of Opensignal, commented, "It is the first time a country has surpassed the 100 Mbps average speed barrier." South Korea also ranked first in overall gaming and video streaming service experience.
Other countries competing for the title of "world's first 5G commercialization" remain outside the top 10. The United States ranks 30th in average download speed. The United Kingdom, which was the third country worldwide to successfully commercialize 5G, ranks 24th in overall download speed, remaining outside the top 20. Japan also ranks 10th in overall download speed, showing a significant gap with South Korea.
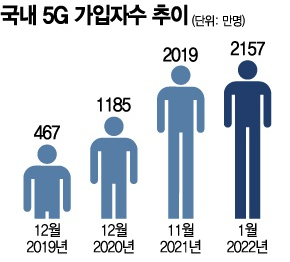
5G service users account for 40% of the entire population. As of the end of January, the number of 5G wireless communication service subscribers reached 21,566,928. Following 20.19 million in November last year and 20.91 million in December, the number exceeded 21.56 million in January this year, increasing by at least 600,000 subscribers each month. SK Telecom was the first among the three major telecom companies to reach 10 million 5G subscribers, followed by KT (6.56 million) and LG Uplus (4.75 million). The average 5G coverage area of the three carriers also increased more than threefold from the previous year to 19,044 km². The average download transmission speed of the three companies rose by 16.1% year-on-year to 801.48 Mbps.
5G Quality Issues Remain a Challenge
Consumer complaints regarding 5G quality are a common challenge shared by South Korea and other major countries. According to data obtained by Rep. Kim Young-sik's office of the People Power Party through the Ministry of Science and ICT, as of the end of 2021, out of a total of 198,832 completed 5G base stations, 45.5% or 90,489 were concentrated in the Seoul metropolitan area. When expanded to include the Seoul metropolitan area plus six major metropolitan cities, the proportion rises to 68.2%. There are 13 local governments where fewer than 10 5G base stations have been installed, making 5G service practically unavailable, especially in rural farming and fishing villages. Lawsuits involving 5G consumers numbering in the thousands are also ongoing.
However, the market points out that the burden of capital expenditure (CAPEX) is a common concern for the telecommunications industry. A telecom industry official said, "5G investment costs are still rapidly increasing, but since the influx is mainly from existing subscriber conversions rather than new subscribers, profitability is declining, increasing the burden of capital investment," adding, "This is why discussions about slowing down investment are emerging." Yago Tenorio, Head of Network Architecture at Vodafone Europe, said, "It is clear that telecom companies will gain the greatest benefits from the expansion of 5G services," but added, "This may be 10 years from now, but it is the right direction for the industry to move forward."
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.











