Interest Coverage Ratio Below 1 Among External Audit Firms
50.5% Possibility This Year if COVID-19 Impact Continues
‘At-Risk Companies’ with Interest Coverage Ratio Below 1 for 3 Consecutive Years Steadily Increasing
Effects of US-China Trade War and COVID-19 Impact
Likely to Keep Rising from 14.2% in 2018
[Asia Economy Reporter Kim Eun-byeol] Amid the ongoing novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) crisis, the financial soundness of domestic companies is rapidly deteriorating. Although the government has injected over 100 trillion won to prevent mass corporate bankruptcies, companies that were already financially distressed before COVID-19 are surviving only through loans. There are concerns that the large-scale funding aimed at mitigating the economic shock may also hinder natural restructuring. If financial institutions stop extending loans and suspending interest payments, many companies could receive an immediate "death sentence," raising fears of a credit crisis.
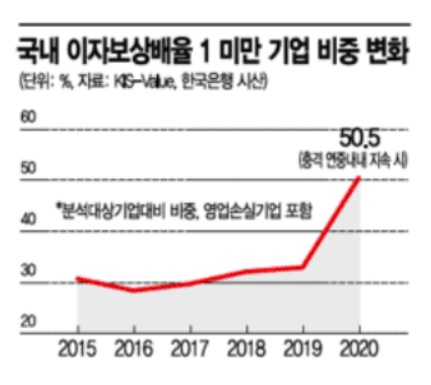
According to the Bank of Korea on the 16th, among 20,693 externally audited companies, the proportion of companies unable to cover even their interest expenses with operating profit (interest coverage ratio below 1) is expected to reach about half this year. This figure was estimated under the scenario that the COVID-19 shock would persist throughout the year, as projected by the Bank of Korea in June. Recently, despite the spread of COVID-19, economic lockdowns have been lifted, showing a decoupling phenomenon, which may result in less corporate shock than expected. However, the proportion of financially vulnerable companies is expected to increase compared to last year. Until last year, the proportion of companies with an interest coverage ratio below 1 remained in the 30% range.
The proportion of marginal companies (zombie companies), defined as those with an interest coverage ratio below 1 for three consecutive years, is also expected to increase rapidly. According to the Bank of Korea, as of 2018, marginal companies accounted for 14.2% (3,236 companies) of externally audited companies. Due to the export impact from the US-China trade war last year and the COVID-19 shock this year, an increase in the proportion of marginal companies is inevitable for the time being. Previously, the Federation of Korean Industries estimated the proportion of marginal companies at 17.9% last year.
The problem is that marginal companies are unlikely to normalize even after the COVID-19 crisis ends. According to analysis by Song Sang-yoon, a senior researcher at the Bank of Korea Economic Research Institute, the proportion of chronic marginal companies increased from 4.2% in 2010 to 5.8% in 2018. Marginal companies can hinder the movement of resources to more productive normal companies, thereby eroding the overall labor productivity of the economy.
Researcher Song stated, "If marginal companies disappear, the average labor productivity of South Korea's manufacturing sector from 2010 to 2018 would increase by 4.3%."
◇Terminology Explanation
◆Marginal companies (zombie companies) = Companies with an interest coverage ratio (operating profit divided by interest expenses) below 1 for three consecutive years. These are companies that have been unable to fully pay their interest expenses with earnings for three years straight.
© The Asia Business Daily(www.asiae.co.kr). All rights reserved.